2019 ATB
For each electricity generation technology in the ATB, this website provides:
- Capital expenditures (CAPEX): the definition of CAPEX used in the ATB and the historical trends, current estimates, and future projections of CAPEX used in the ATB
- Operations and maintenance (O&M) costs: the definition of O&M and the current estimates and future projections of O&M used in the ATB
- Capacity factor (CF): the definition of CF and the historical trends, current estimates, and future projections of CF used in the ATB
- Future cost and performance methods: an outline of the methodology used to make the projections of future cost and performance in the ATB for Constant, Mid, and Low technology cost cases
- Levelized cost of energy (LCOE): metric that combines CAPEX, O&M, CF, and projections for Constant, Mid, and Low technology cost cases for illustration of the combined effect of the primary cost and performance components and discussion of technology advances that yield future projections
- Financing assumptions: development of technology-specific interest rate on debt, return on equity, and debt-to-equity ratios and their impact on LCOE are documented in each technology section, where applicable, and summarized here.
Electricity generation technologies are selected on the left side of the screen, and the topics highlighted above can be selected using the drop-down menu at the top right of the screen.
Guidelines for using and interpreting ATB content and comparisons to other literature are provided. LCOE accounts for many variables important to determining the competitiveness of building and operating a specific technology (e.g., upfront capital costs, capacity factor, and cost of financing); however, it does not necessarily demonstrate which technology in a given place and time would provide the lowest cost option for the electricity grid. Such analysis is performed using electric sector models such as the Regional Energy Deployment Systems (ReEDS) model and corresponding analysis results such as the NREL Standard Scenarios.
The NREL Standard Scenarios, a companion product to the ATB, provides a suite of electric sector scenarios and associated assumptions, including technology cost and performance assumptions from the ATB.
ATB data sources and references are also provided for each technology. All dollar values are presented in 2017 U.S. dollars, unless noted otherwise.
Additional information is available here: About the 2019 ATB.
Geothermal
Geothermal technology cost and performance projections have been updated with analysis and results from the GeoVision: Harnessing the Heat Beneath our Feet report (DOE, 2019). The GeoVision report is a collaborative multiyear effort with contributors from industry, academia, national laboratories, and federal agencies. The analysis in the report updates resource potential estimates as well as current and projected capital and O&M costs based on rigorous, bottom-up modeling.
Representative Technology
Hydrothermal geothermal technologies encompass technologies for exploring for the resource, drilling to access the resource, and building power plants to convert geothermal energy to electricity. Technology costs depend heavily on the hydrothermal resource temperature and well productivity and depth, so much so that project costs are site-specific and applying a "typical" cost to any given site would be inaccurate. The 2019 ATB uses scenarios developed by the DOE Geothermal Technology Office (Mines, 2013) for representative binary and flash hydrothermal power plant technologies. The first scenario assumes a 175°C resource at a depth of 1.5 km with wells producing an average of 110 kg/s of geothermal brine supplied to a 30-MWe binary (organic Rankine cycle) power plant. The second scenario assumes a 225°C resource at a depth of 2.5 km with wells producing 80 kg/s of geothermal brine supplied to a 40-MWe dual-flash plant. These are mid-grade or "typical" temperatures and depths for binary and flash hydrothermal projects. The ReEDS model uses the full hydrothermal supply curve. The 2019 ATB representative technologies fall in the middle or near the end of the hydrothermal resources typically deployed in ReEDS model runs.
Resource Potential
The hydrothermal geothermal resource is concentrated in the western United States. The total mean potential is 39,090 MW: 9,057 MW identified and 30,033 MW undiscovered (USGS, 2008). The resource potential identified by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS, 2008) at each site is based on available reservoir thermal energy information from studies conducted at the site. The undiscovered hydrothermal technical potential estimate is based on a series of GIS statistical models for the spatial correlation of geological factors that facilitate the formation of geothermal systems.
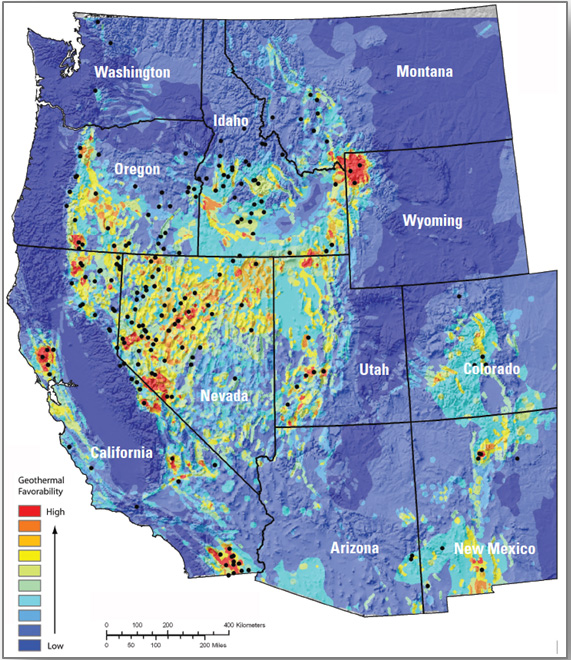
The U.S. Geological Survey resource potential estimates for hydrothermal were used with the following modifications:
- Installed capacity of about 3 GW in 2016 is excluded from the resource potential.
- Resources on federally protected and U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) lands, where development is highly restricted are excluded from the resource potential, as are resources on lands where significant barriers that prevent or inhibit development of geothermal projects were identified by Augustine, Ho, and Blair (2019).
Renewable energy technical potential, as defined by Lopez et al. (2012), represents the achievable energy generation of a particular technology given system performance, topographic limitations, and environmental and land-use constraints. The primary benefit of assessing technical potential is that it establishes an upper-boundary estimate of development potential. It is important to understand that there are multiple types of potential-resource, technical, economic, and market (see NREL: "Renewable Energy Technical Potential").
Base Year and Future Year Projections Overview
The Base Year cost and performance estimates are calculated using Geothermal Electricity Technology Evaluation Model (GETEM), a bottom-up cost analysis tool that accounts for each phase of development of a geothermal plant (DOE "Geothermal Electricity Technology Evaluation Model").
- Cost and performance data for hydrothermal generation plants are estimated for each potential site using GETEM. Model results are based on resource attributes (e.g., estimated reservoir temperature, depth, and potential) of each site. GETEM inputs are derived from the Business-as-Usual (BAU) scenario from GeoVision ( (DOE, 2019), (Augustine, Ho, & Blair, 2019)).
- Site attribute values are from (USGS, 2008) for identified resource potential and from capacity-weighted averages of site attribute values of nearby identified resources for undiscovered resource potential.
- GETEM is used to estimate CAPEX, O&M, and parasitic plant losses that affect net energy production.
Capacity factor and O&M costs for plants installed in future years are unchanged from the Base Year. Projections for hydrothermal and EGS technologies are equivalent.
- Constant Technology Cost Scenario: no change in CAPEX, O&M, or capacity factor from 2015 to 2050; consistent across all renewable energy technologies in the ATB
- Mid Technology Cost Scenario: CAPEX cost reduction based on assumed minimum learning as implemented in AEO (EIA, 2015): 10% by 2035; this corresponds to a 0.5% annual improvement in CAPEX, which is assumed to continue on through 2050
- Low Technology Cost Scenario: CAPEX based on the Technology Improvement scenario from GeoVision Study ( (DOE, 2019); (Augustine, Ho, & Blair, 2019)); cost and technology improvements change linearly from present values and are fully achieved by 2030.
Representative Technology
As with cost for projects that use hydrothermal resources, EGS resource project costs depend so heavily on the hydrothermal resource temperature and well productivity and depth that project costs are site-specific. The 2019 ATB uses scenarios developed by the DOE Geothermal Technology Office (Mines, 2013) for representative binary and flash EGS power plants assuming current (immature) EGS technology performance metrics. The first scenario assumes a 175°C resource at a depth of 3 km with wells producing an average of 40 kg/s of geothermal brine supplied to a 25-MWe binary (organic Rankine cycle) power plant. The second scenario assumes a 250°C resource at a depth of 3.5 km with wells producing 40 kg/s of geothermal brine supplied to a 30-MWe dual-flash plant. These temperatures and depths are at the low-cost end of the EGS supply curve and would be some of the first developed. The ReEDS model uses the full EGS supply curve. Neither of these technologies is typically used.
Resource Potential
The enhanced geothermal system (EGS) resource is concentrated in the western United States. The total potential is greater than 100,000 MW: 1,493 MW of near-hydrothermal field EGS (NF-EGS) and the remaining potential comes from deep EGS.
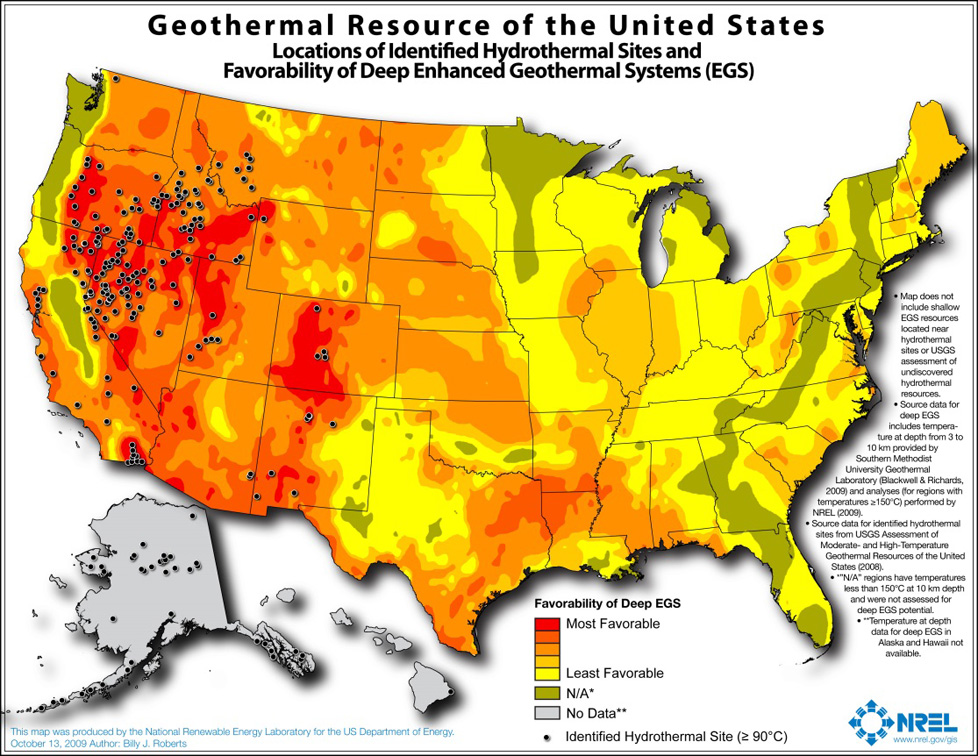
Renewable energy technical potential as defined by Lopez et al. (2012) represents the achievable energy generation of a particular technology given system performance, topographic limitations, environmental, and land-use constraints. The primary benefit of assessing technical potential is that it establishes an upper-boundary estimate of development potential. It is important to understand there are multiple types of potential-resource, technical, economic, and market (see NREL: "Renewable Energy Technical Potential").
Base Year and Future Year Projections Overview
The Base Year cost and performance estimates are calculated using the Geothermal Electricity Technology Evaluation Model (GETEM), a bottom-up cost analysis tool that accounts for each phase of development of a geothermal plant (DOE "Geothermal Electricity Technology Evaluation Model").
- Cost and performance data for EGS generation plants are estimated for each potential site using GETEM. Model results based on resource attributes (e.g., estimated reservoir temperature, depth, and potential) of each site. GETEM inputs are derived from the GeoVision BAU scenario ( (DOE, 2019), (Augustine, Ho, & Blair, 2019)).
- Approaches to restrict resource potential to about 500 GW based on USGS analysis may be implemented in the future.
- GETEM is used to estimate CAPEX and O&M and parasitic plant losses that affect net energy production.
Capacity factor and O&M costs for plants installed in future years are unchanged from the Base Year. Projections for hydrothermal and enhanced geothermal system technologies are equivalent.
- Constant Technology Cost Scenario: no change in CAPEX, O&M, or capacity factor from 2015 to 2050, consistent across all renewable energy technologies in the ATB
- Mid Technology Cost Scenario: CAPEX cost reduction based on assumed minimum learning as implemented in AEO (EIA, 2015): 10% by 2035; this corresponds to a 0.5% annual improvement in CAPEX, which is assumed to continue on through 2050.
- Low Technology Cost Scenario: CAPEX based on the GeoVision Technology Improvement scenario ( (DOE, 2019), (Augustine, Ho, & Blair, 2019)). Cost and technology improvements decrease linearly from present values and are fully achieved by 2030.
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year. These expenditures include the geothermal generation plant, the balance of system (e.g., site preparation, installation, and electrical infrastructure), and financial costs (e.g., development costs, onsite electrical equipment, and interest during construction) and are detailed in CAPEX Definition. In the ATB, CAPEX reflects typical plants and does not include differences in regional costs associated with labor, materials, taxes, or system requirements. The related Standard Scenarios product uses Regional CAPEX Adjustments. The range of CAPEX demonstrates variation with resource in the contiguous United States.
The following figure shows the Base Year estimate and future year projections for CAPEX costs. Three cost scenarios are represented: Constant, Mid, and Low technology cost. The estimate for a given year represents CAPEX of a new plant that reaches commercial operation in that year.
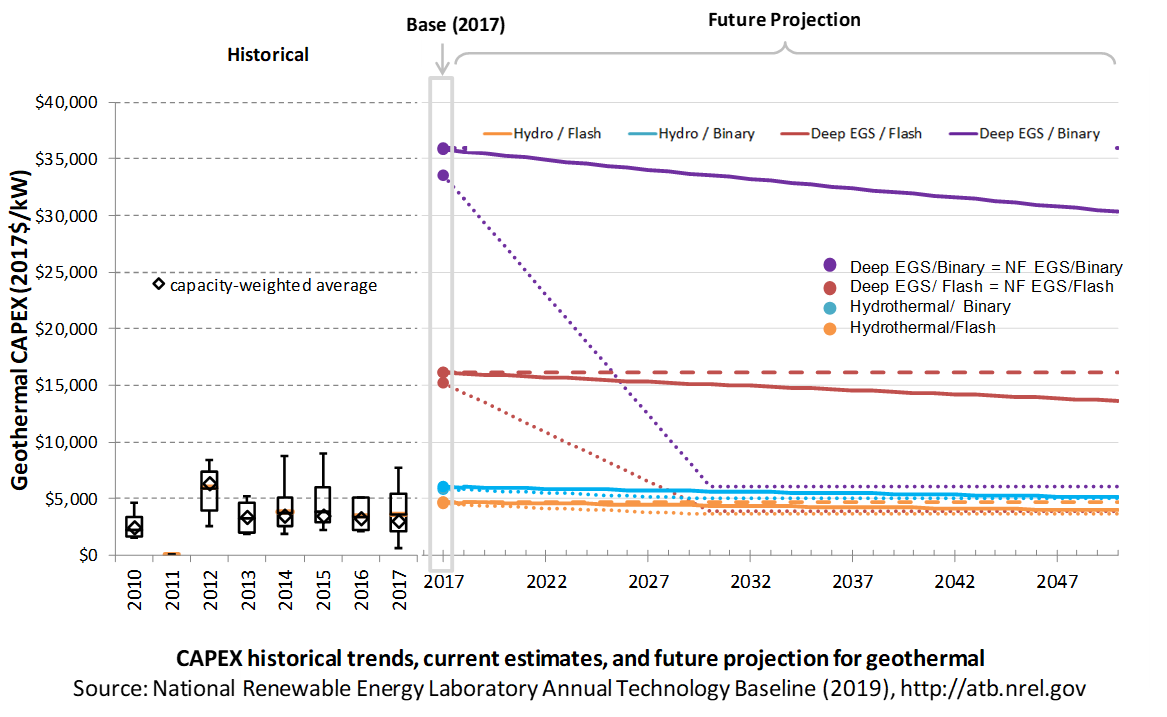
Base Year Estimates
For illustration in the ATB, six representative geothermal plants are shown. Two energy conversion processes are common: binary organic Rankine cycle and flash.
- Binary plants use a heat exchanger to transfer geothermal energy to an organic Rankine cycle. This technology generally applies to lower-temperature systems. These systems have higher CAPEX than flash systems because of the increased number of components, their lower-temperature operation, and a general requirement that a number of wells be drilled for a given power output.
- Flash plants create steam directly from the thermal fluid through a pressure change. This technology generally applies to higher-temperature systems. Due to the reduced number of components and higher-temperature operation, these systems generally produce more power per well, thus reducing drilling costs. These systems generally have lower CAPEX than binary systems.
Examples using each of these plant types in each of the three resource types (hydrothermal, NF-EGS, and deep EGS) are shown in the ATB.
Costs are for new or greenfield hydrothermal projects, not for re-drilling or additional development/capacity additions at an existing site.
Characteristics for the six examples of plants representing current technology were developed based on discussion with industry stakeholders. The CAPEX estimates were generated using GETEM. CAPEX for NF-EGS and EGS are equivalent.
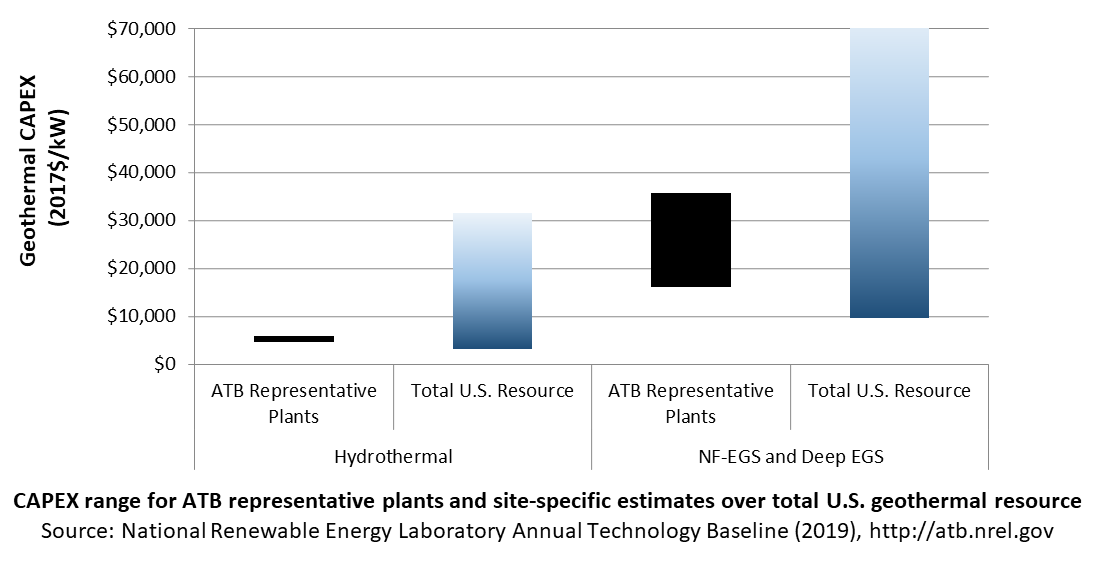
The following table shows the range of OCC associated with the resource characteristics for potential sites throughout the United States.
| Temp (°C) | >=200C | 150-200 | 135-150 | <135 | |
| Hydrothermal | Number of identified sites | 21 | 23 | 17 | 59 |
| Total capacity (MW) | 15,338 | 2,991 | 820 | 4,632 | |
| Average OCC ($/kW) | 3,906 | 7,720 | 8,794 | 16,248 | |
| Min OCC ($/kW) | 3,000 | 4,140 | 7,004 | 10,950 | |
| Max OCC ($/kW) | 5,491 | 29,135 | 11,027 | 21,349 | |
| Example of plant OCC ($/kW) | 4,229 | 5,455 | |||
| NF-EGS | Number of sites | 12 | 20 | ||
| Total capacity (MW) | 787 | 596 | |||
| Average OCC ($/kW) | 11,041 | 26,077 | |||
| Min OCC ($/kW) | 8,778 | 18,172 | |||
| Max OCC ($/kW) | 18,009 | 39,987 | |||
| Example of plant OCC ($/kW) | 14,512 | 32,268 | |||
| Deep EGS (3-6 km) | Number of sites | n/a | n/a | ||
| Total capacity (MW) | 100,000+ | ||||
| Average OCC ($/kW) | 28,418 | 60,170 | |||
| Min OCC ($/kW) | 18,320 | 39,329 | |||
| Max OCC ($/kW) | 54,047 | 77,983 | |||
| Example of plant OCC ($/kW) | 14,512 | 32,268 | |||
Future Year Projections
Projection of future geothermal plant CAPEX for the Low case is based on the GeoVision Technology Improvement scenario (DOE, 2019).
A detailed description of the methodology for developing future year projections is found in Projections Methodology.
Technology innovations that could impact future O&M costs are summarized in LCOE Projections.
CAPEX Definition
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year.
For the ATB – and based on (EIA, 2016) and GETEM component cost calculations – the geothermal plant envelope is defined to include:
- Geothermal generation plant
- Exploration, confirmation drilling, well field development, reservoir stimulation (EGS), plant equipment, and plant construction
- Power plant equipment, well-field equipment, and components for wells (including dry/non-commercial wells)
- Balance of system (BOS)
- Installation and electrical infrastructure, such as transformers, switchgear, and electrical system connecting turbines to each other and to the control center
- Project indirect costs, including costs related to engineering, distributable labor and materials, construction management start up and commissioning, and contractor overhead costs, fees, and profit
- Financial costs
- Owners' costs, such as development costs, preliminary feasibility and engineering studies, environmental studies and permitting, legal fees, insurance costs, and property taxes during construction
- Electrical interconnection and onsite electrical equipment (e.g., switchyard), a nominal-distance spur line (<1 mile), and necessary upgrades at a transmission substation; distance-based spur line cost (GCC) not included in the ATB
- Interest during construction estimated based on four-year and five-year duration for hydrothermal and EGS respectively (for the low scenario) and an eight-year duration and ten-year duration for hydrothermal and EGS respectively (for the mid- and constant-scenario) accumulated at different intervals for hydro and EGS based on scheduled at outlined by the GeoVision Study (ConFinFactor).
CAPEX can be determined for a plant in a specific geographic location as follows:
Regional cost variations and geographically specific grid connection costs are not included in the ATB (CapRegMult = 1; GCC = 0). In the ATB, the input value is overnight capital cost (OCC) and details to calculate interest during construction (ConFinFactor).
In the ATB, CAPEX is shown for six representative plants. Examples of CAPEX for binary organic Rankine cycle and flash energy conversion processes in each of three geothermal resource types are presented. CAPEX estimates for all hydrothermal NF-EGS potential results in a CAPEX range that is much broader than that shown in the ATB. It is unlikely that all the resource potential will be developed due to the high costs for some sites. Regional cost effects and distance-based spur line costs are not estimated.
Standard Scenarios Model Results
ATB CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor assumptions for the Base Year and future projections through 2050 for Constant, Mid, and Low technology cost scenarios are used to develop the NREL Standard Scenarios using the ReEDS model. See ATB and Standard Scenarios.
The ReEDS model represents cost and performance for hydrothermal, NF-EGS, and EGS potential in 5 bins for each of 134 geographic regions, resulting in a greater CAPEX range in the reference supply curve than what is shown in examples in the ATB.
CAPEX in the ATB does not represent regional variants (CapRegMult) associated with labor rates, material costs, etc., and neither does the ReEDS model.
CAPEX in the ATB does not include geographically determined spur line (GCC) from plant to transmission grid, and neither does the ReEDS model.
Operations and maintenance (O&M) costs represent average annual fixed expenditures (and depend on rated capacity) required to operate and maintain a hydrothermal plant over its lifetime of 30 years (plant and reservoir), including:
- Insurance, taxes, land lease payments, and other fixed costs
- Present value and annualized large component overhaul or replacement costs over technical life (e.g., downhole pumps)
- Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance of geothermal plant components and well field components over the technical lifetime of the plant and reservoir.
The following figure shows the Base Year estimate and future year projections for fixed O&M (FOM) costs. Three cost scenarios are represented. The estimate for a given year represents annual average FOM costs expected over the technical lifetime of a new plant that reaches commercial operation in that year.
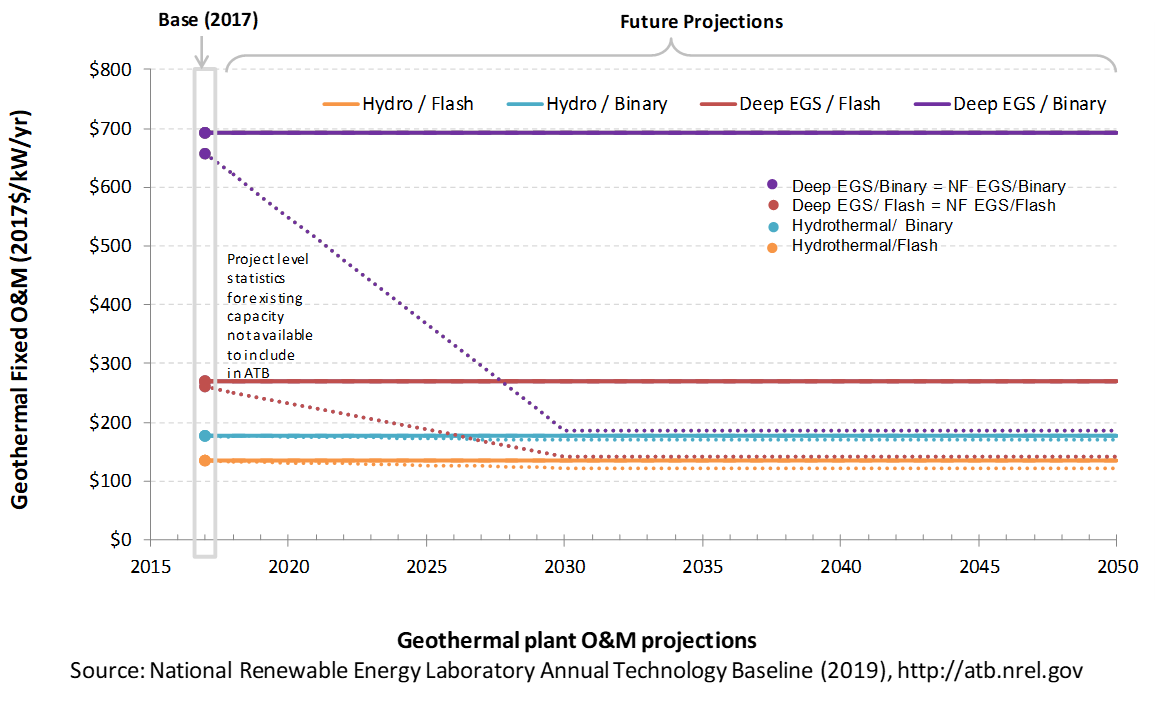
Base Year Estimates
FOM is estimated for each example of a plant based on technical characteristics.
GETEM is used to estimate FOM for each of the six representative plants. FOM for NF-EGS and EGS are equivalent.
Future Year Projections
Future FOM cost reductions are based on results from the GeoVision scenario (DOE, 2019) and are described in detail in Augustine, Ho, and Blair (2019).
Capacity Factor: Expected Annual Average Energy Production Over Lifetime
The capacity factor represents the expected annual average energy production divided by the annual energy production, assuming the plant operates at rated capacity for every hour of the year. It is intended to represent a long-term average over the technical lifetime of the plant. It does not represent interannual variation in energy production. Future year estimates represent the estimated annual average capacity factor over the technical lifetime of a new plant installed in a given year.
Geothermal plant capacity factor is influenced by diurnal and seasonal air temperature variation (for air-cooled plants), technology (e.g., binary or flash), downtime, and internal plant energy losses.
The following figure shows a range of capacity factors based on variation in the resource for plants in the contiguous United States. The range of the Base Year estimates illustrates Binary or Flash geothermal plants. Future year projections for the Constant, Mid, and Low technology cost scenarios are unchanged from the Base Year. Technology improvements are focused on CAPEX cost elements.
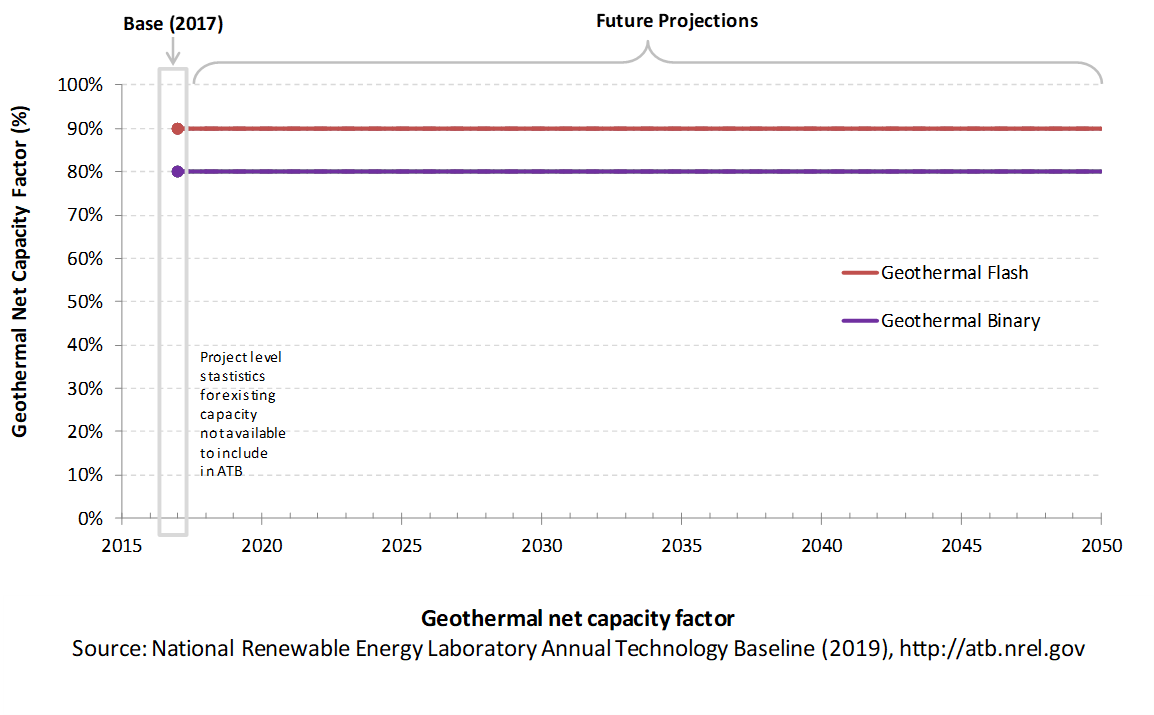
Base Year Estimate
The capacity factor estimates are developed using GETEM at typical design air temperature and based on design plant capacity net losses. An additional reduction is applied to approximate potential variability due to seasonal temperature effects.
Some geothermal plants have experienced year-on-year reductions in energy production, but this is not consistent across all plants. No approximation of long-term degradation of energy output is assumed.
Ongoing work at NREL and the Idaho National Laboratory is helping improve capacity factor estimates for geothermal plants. As this work progresses, it will be incorporated into future versions of the ATB.
Future Year Projections
Capacity factors remain unchanged from the Base Year through 2050. Technology improvements are focused on CAPEX costs. Estimates of capacity factor for geothermal plants in the ATB represent typical operation. The dispatch characteristics of these systems are valuable to the electric system to manage changes in net electricity demand. Actual capacity factors will be influenced by the degree to which system operators call on geothermal plants to manage grid services.
Plant Cost and Performance Projections Methodology
The site-specific nature of geothermal plant cost, the relative maturity of hydrothermal plant technology, and the very early stage development of EGS technologies make cost projections difficult. No thorough literature reviews have been conducted for cost reduction of hydrothermal geothermal technologies or EGS technologies. However, the GeoVision BAU scenario is based on a bottom-up analysis of costs and performance improvements. The inputs for the BAU scenario were developed by the national laboratories as part of the GeoVision effort, and it was reviewed by industry experts.
Projection of future geothermal plant CAPEX for the Low cost case is based on the GeoVision Technology Improvement scenario. It assumes that cost and technology improvements are achieved by 2030 and that costs decrease linearly from present values to the 2030 projected values. The Mid cost case is based on minimum learning rates as implemented in AEO (EIA, 2015): 10% by 2035. This corresponds to a 0.5% annual improvement in CAPEX, which is assumed to continue on through 2050. The Constant technology cost scenario retains all cost and performance assumptions equivalent to the Base Year through 2050.
Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) Projections
Levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is a simple metric that combines the primary technology cost and performance parameters: CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor. It is included in the ATB for illustrative purposes. The ATB focuses on defining the primary cost and performance parameters for use in electric sector modeling or other analysis where more sophisticated comparisons among technologies are made. The LCOE accounts for the energy component of electric system planning and operation. The LCOE uses an annual average capacity factor when spreading costs over the anticipated energy generation. This annual capacity factor ignores specific operating behavior such as ramping, start-up, and shutdown that could be relevant for more detailed evaluations of generator cost and value. Electricity generation technologies have different capabilities to provide such services. For example, wind and PV are primarily energy service providers, while the other electricity generation technologies such as geothermal, can provide capacity and flexibility services in addition to energy. These capacity and flexibility services are difficult to value and depend strongly on the system in which a new generation plant is introduced. These services are represented in electric sector models such as the ReEDS model and corresponding analysis results such as the Standard Scenarios.
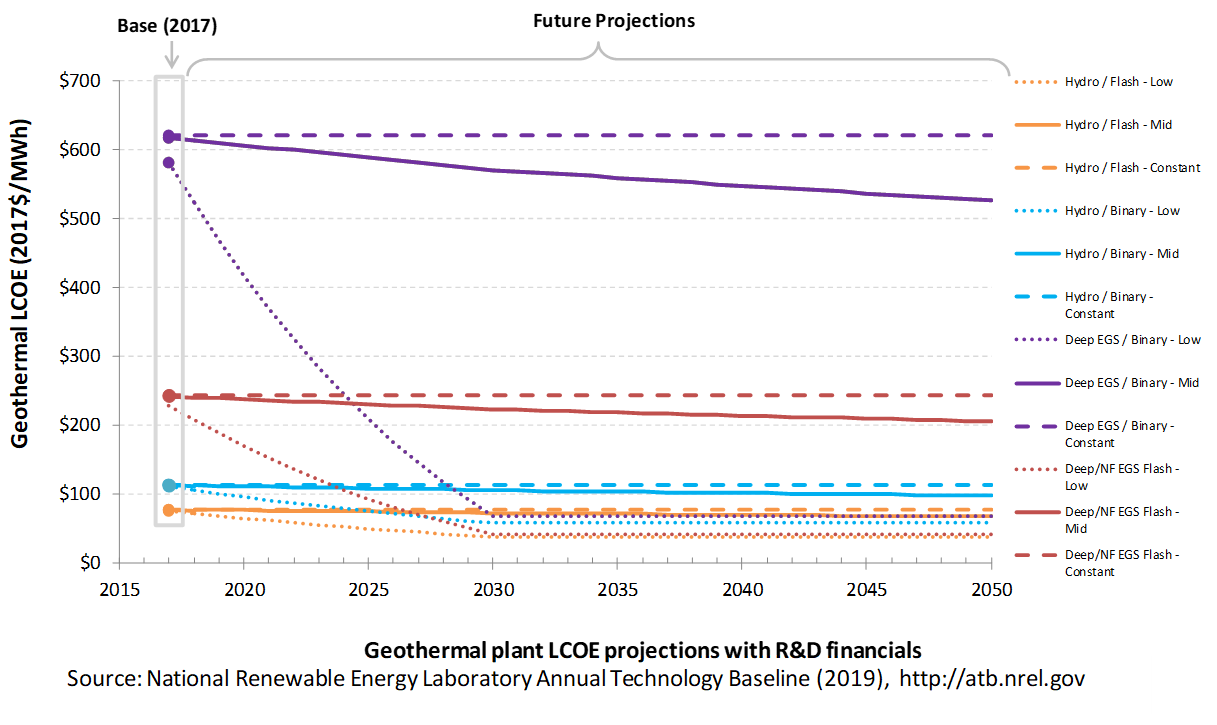
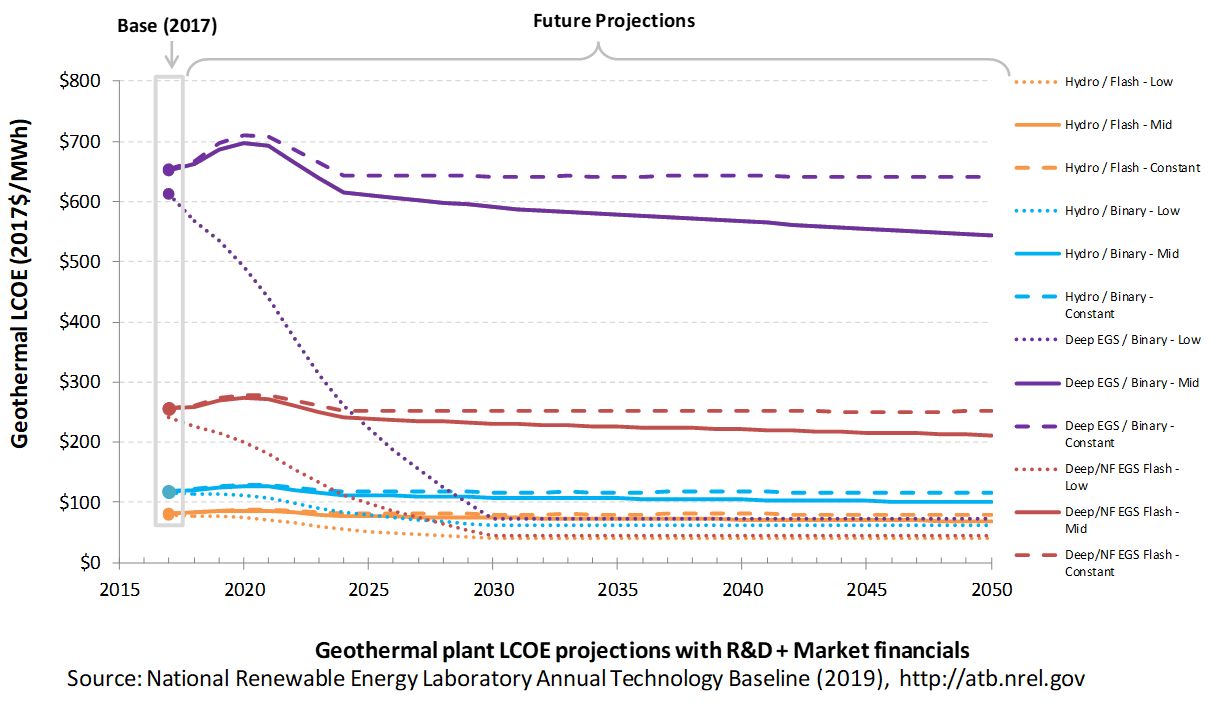
The following three figures illustrate LCOE, which includes the combined impact of CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor projections for geothermal across the range of resources present in the contiguous United States. For the purposes of the ATB, the costs associated with technology and project risk in the U.S. market are represented in the financing costs but not in the upfront capital costs (e.g., developer fees and contingencies). An individual technology may receive more favorable financing terms outside the United States, due to less technology and project risk, caused by more project development experience (e.g., offshore wind in Europe) or more government or market guarantees. The R&D Only LCOE sensitivity cases present the range of LCOE based on financial conditions that are held constant over time unless R&D affects them, and they reflect different levels of technology risk. This case excludes effects of tax reform, tax credits, technology-specific tariffs, and changing interest rates over time. The R&D + Market LCOE case adds to these financial assumptions: (1) the changes over time consistent with projections in the Annual Energy Outlook and (2) the effects of tax reform, tax credits, and tariffs. The ATB representative plant characteristics that best align with those of recently installed or anticipated near-term geothermal plants are associated with Hydrothermal/Flash. Data for all the resource categories can be found in the ATB Data spreadsheet; for simplicity, not all resource categories are shown in the figures.
R&D Only | R&D + Market
The methodology for representing the CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor assumptions behind each pathway is discussed in Projections Methodology. In general, the degree of adoption of technology innovation distinguishes the Constant, Mid, and Low technology cost scenarios. These projections represent trends that reduce CAPEX and improve performance. Development of these scenarios involves technology-specific application of the following general definitions:
- Constant Technology: Base Year (or near-term estimates of projects under construction) equivalent through 2050 maintains current relative technology cost differences
- Mid Technology Cost Scenario: Technology advances through continued industry growth, public and private R&D investments, and market conditions relative to current levels that may be characterized as "likely" or "not surprising"
- Low Technology Cost Scenario: Technology advances that may occur with breakthroughs, increased public and private R&D investments, and/or other market conditions that lead to cost and performance levels that may be characterized as the " limit of surprise" but not necessarily the absolute low bound.
To estimate LCOE, assumptions about the cost of capital to finance electricity generation projects are required, and the LCOE calculations are sensitive to these financial assumptions. Two project finance structures are used within the ATB:
- R&D Only Financial Assumptions: This sensitivity case allows technology-specific changes to debt interest rates, return on equity rates, and debt fraction to reflect effects of R&D on technological risk perception, but it holds background rates constant at 2017 values from AEO2019 (EIA, 2019) and excludes effects of tax reform, tax credits, and tariffs.
- R&D Only + Market Financial Assumptions: This sensitivity case retains the technology-specific changes to debt interest, return on equity rates, and debt fraction from the R&D Only case and adds in the variation over time consistent with AEO2018, as well as effects of tax reform, tax credits, and technology-specific tariffs. For a detailed discussion of these assumptions, see Changes from 2018 ATB to 2019 ATB.
A constant cost recovery period – over which the initial capital investment is recovered – of 30 years is assumed for all technologies throughout this website, and can be varied in the ATB data spreadsheet.
The equations and variables used to estimate LCOE are defined on the Equations and Variables page. For illustration of the impact of changing financial structures such as WACC, see Project Finance Impact on LCOE. For LCOE estimates for the Constant, Mid, and Low technology cost scenarios for all technologies, see 2019 ATB Cost and Performance Summary.
In general, differences among the technology cost cases reflect different levels of adoption of innovations. Reductions in technology costs reflect the cost reduction opportunities that are listed below.
- Development of exploration and reservoir characterization tools that reduce well-field costs through risk reduction by locating and characterizing low- and moderate-temperature hydrothermal systems prior to drilling
- High-temperature tools and electronics for geothermal subsurface operations
- Development of reservoir engineering techniques and technologies that enable EGS
- More efficient drilling practices and advanced drilling systems such as using flames or lasers to drill through rock; drilling steering technology; and other technologies to reduce drilling costs.
Battery Storage
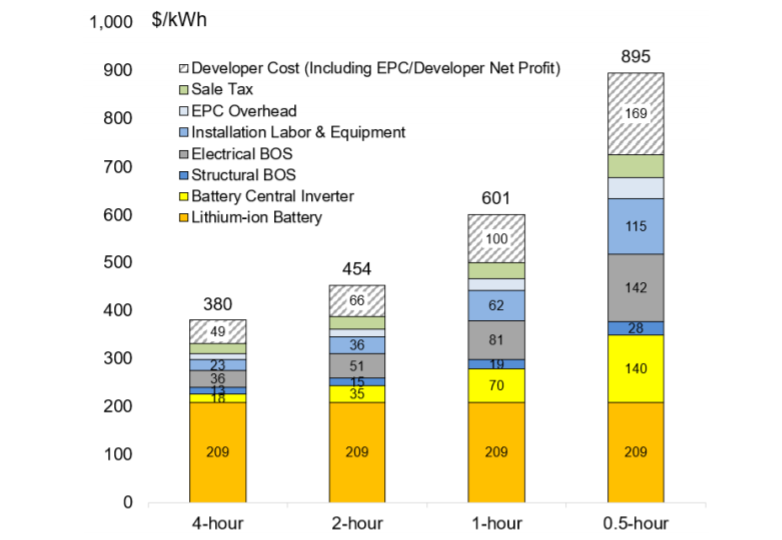
Energy storage technologies are important to document in the ATB because of their potential role in enhancing grid flexibility, especially under scenarios of high penetration of variable renewable technologies. CSP with TES and Hydropower both include storage capabilities, and a variety of other storage technologies could enhance the flexibility of the electrical grid. This section documents assumptions about only one of them: 4-hour, utility-scale, lithium-ion battery storage. NREL has completed recent analysis on ranges of costs related to other battery sizes (Fu, Remo, & Margolis, 2018) with relative costs represented in Figure ES-1 of the report (included below) which looked at 4-hour to 0.5 hour battery duration of utility scale plants.
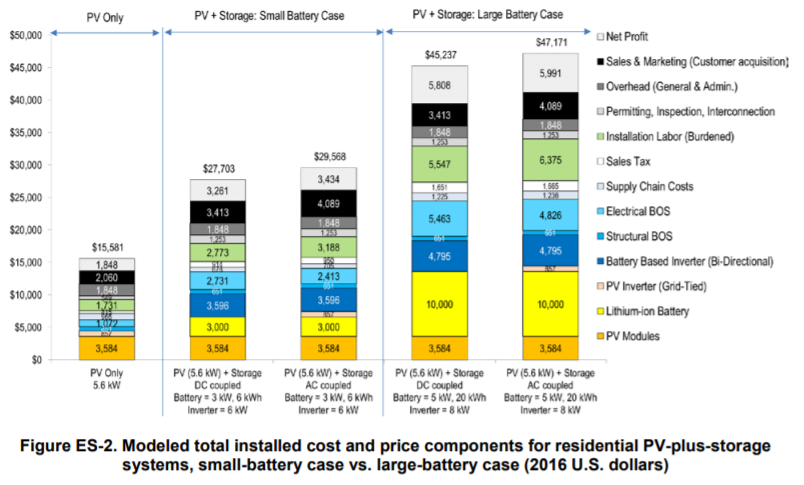
The ATB does not currently have costs for distributed battery storage-either for residential nor commercial applications behind the meter nor for a micro-grid or off-grid application. NREL has completed prior work on residential battery plus solar PV system analysis (Ardani et al., 2017) resulting in a range of costs of PV+battery systems as shown in the figure below. Note these costs are for 2016 and published in 2017, so we anticipate battery costs to be significantly lower currently.
Base Year and Future Year Projections Overview
Battery cost and performance projections are based on a literature review of 25 sources published between 2016 and 2019, as described by Cole and Frazier (2019) . Three different projections from 2017 to 2050 were developed for scenario modeling based on this literature:
- High Technology Cost Scenario: generally based on the maximum of literature projections of future CAPEX and O&M technology pathway analysis; distinct from the Constant technology cost scenarios used among renewable energy technologies in the ATB
- Mid Technology Cost Scenario: generally based on the median of literature projections of future CAPEX and O&M technology pathway analysis
- Low Technology Cost Scenario: generally based on the low bound of literature projections of future CAPEX and O&M technology pathway analysis.
Standard Scenarios Model Results
ATB CAPEX, O&M, and round-trip efficiency assumptions for the Base Year and future projections through 2050 for High, Mid, and Low technology cost scenarios are used to develop the NREL Standard Scenarios using the ReEDS model. See ATB and Standard Scenarios.
Representative Technology
The representative technology was a utility-scale lithium-ion battery storage system with a 15-year life and a 4-hour rating, meaning it could discharge at its rated capacity for four hours as described by Cole and Frazier (2019) . Within the ATB spreadsheet, the costs are separated into energy and power cost estimates, which allow capital costs to be constructed for durations other than 4 hours according to the following equation:
For more information on the power vs. energy cost breakdown, see Cole and Frazier (2019) .
Capital Expenditures (CAPEX): Historical Trends, Current Estimates, and Future Projections
Recent Trends
Costs of lithium-ion battery storage systems have declined rapidly in recent years, prompting greater interest in utility-scale applications.
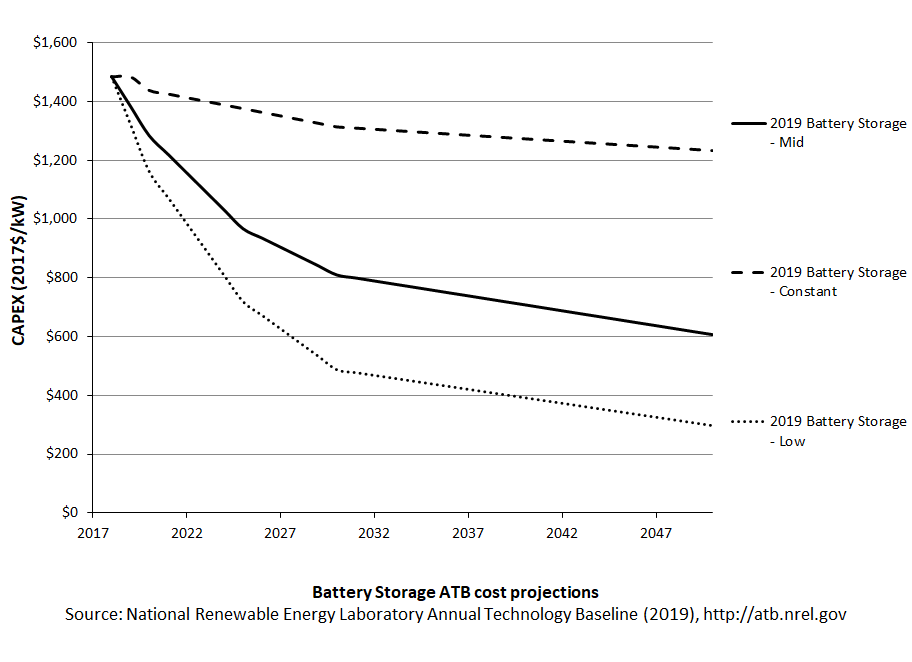
Base Year Estimates
The Base Year cost estimate is taken from Fu, Remo, and Margolis (2018). Comparisons to other reported costs for 2018 are included in Cole, Wesley & Frazier, A. Will (2019). Although the ATB uses a 2017 Base Year, the 2018 estimate based on the literature is the first year reported in the ATB, with a value of $1,484/kW in 2017 dollars.
Future Projections
Future projections are taken from Cole and Frazier (2019), which generally used the median of published cost estimates to develop a Mid Technology Cost Scenario and the minimum values to develop a Low Technology Cost Scenario. Analysts' judgment was used to select the long-term projections to 2050 from a sparse data set.
CAPEX Definition
The literature review does not enumerate elements of the capital cost of lithium-ion batteries (Cole, Wesley & Frazier, A. Will, 2019). However, the NREL storage cost report does detail a breakdown of capital costs with the actual battery pack being the largest component but significant other costs are also included. This breakdown is different if the battery is part of a hybrid system with solar PV. These relative costs for utility-scale standalone battery and battery + PV are demonstrated in the figure below (Fu, Remo, & Margolis, 2018).
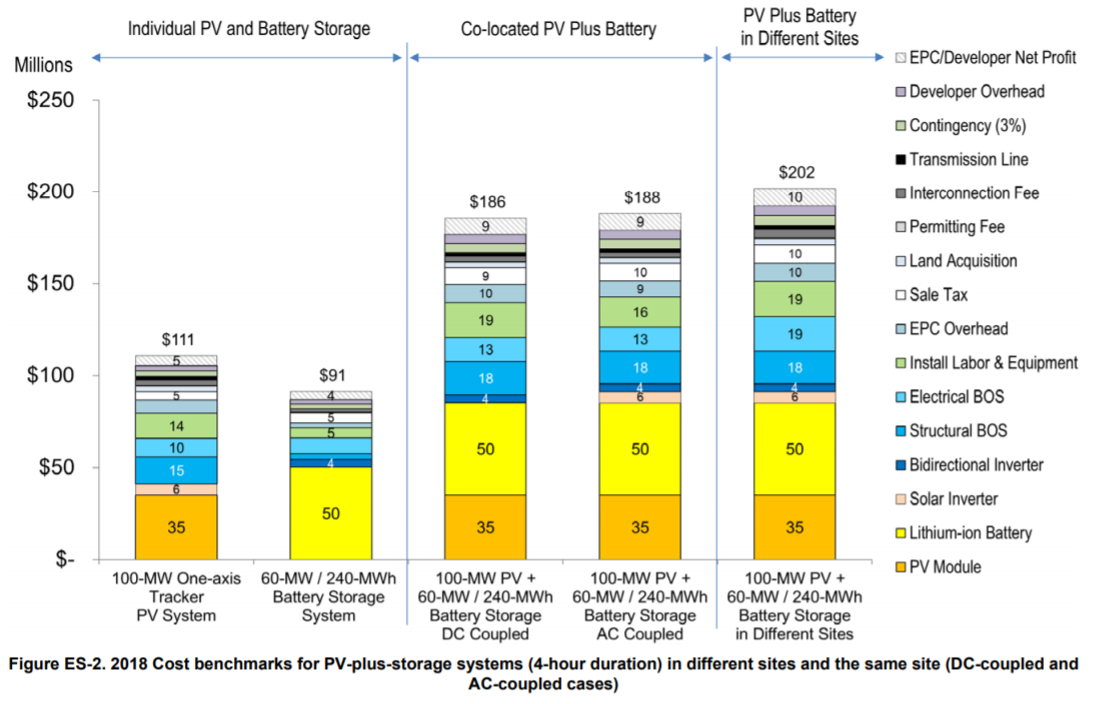
Operation and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
Base Year Estimates
Cole and Frazier (2019) assumed no variable operation and maintenance (VOM) cost. All operating costs were instead represented using fixed operation and maintenance (FOM) costs. The FOM costs include augmentation costs needed to keep the battery system operating at rated capacity for its lifetime. In the ATB, FOM is defined as the value needed to compensate for degradation to enable the battery system to have a constant capacity throughout its life. The literature review states that FOM costs are estimated at 2.5% of the $/kW capital costs.
Future Projections
In the ATB, the FOM cost remains constant at 2.5% of capital costs in all scenarios.
Round-trip efficiency is the ratio of useful energy output to useful energy input. Cole and Frazier (2019) identified 85% as a representative round-trip efficiency, and the ATB adopts this value.
Coal
The ATB includes three coal power plant types: coal-new, coal-IGCC, and coal-CCS. The cost and performance characteristics of these plants are adapted from EIA data rather than derived from original analysis.
Capital Expenditures (CAPEX): Historical Trends, Current Estimates, and Future Projections
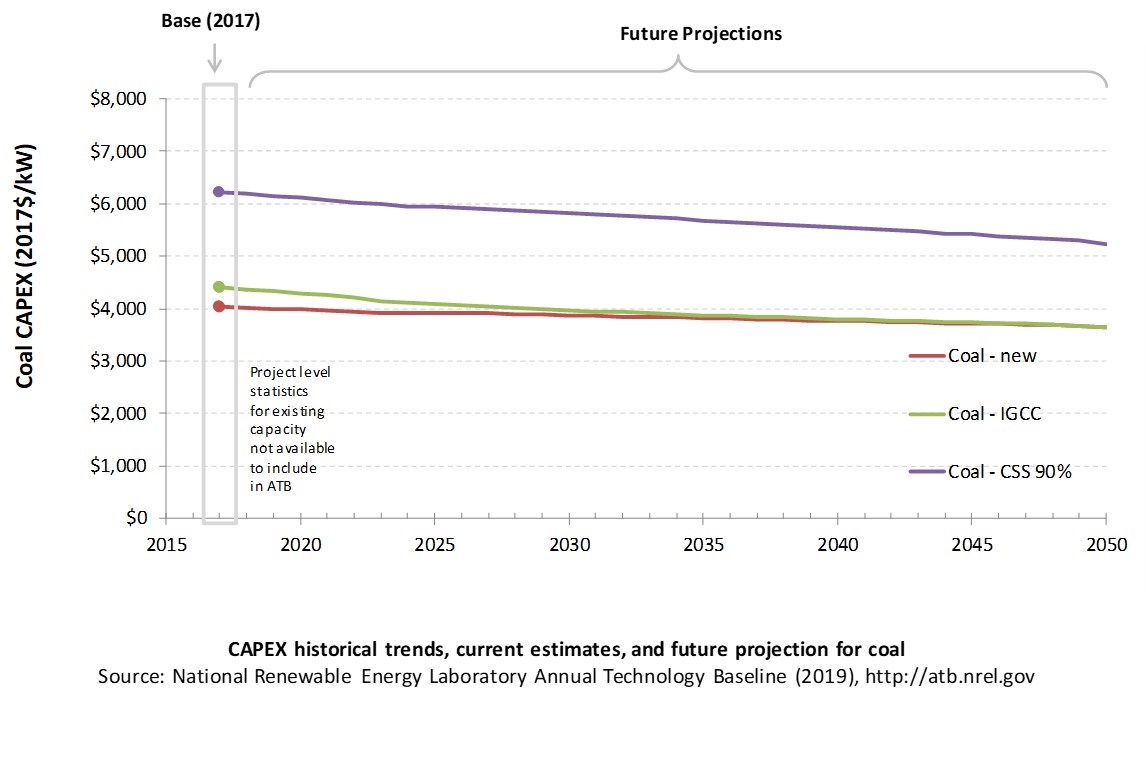
Coal power plant CAPEX is taken from the AEO2019 Reference Scenario (EIA, 2019a) with the adjustments discussed in the CAPEX definition section. The ATB includes only a single CAPEX projection for each type of coal plant.
Comparison with Other Sources
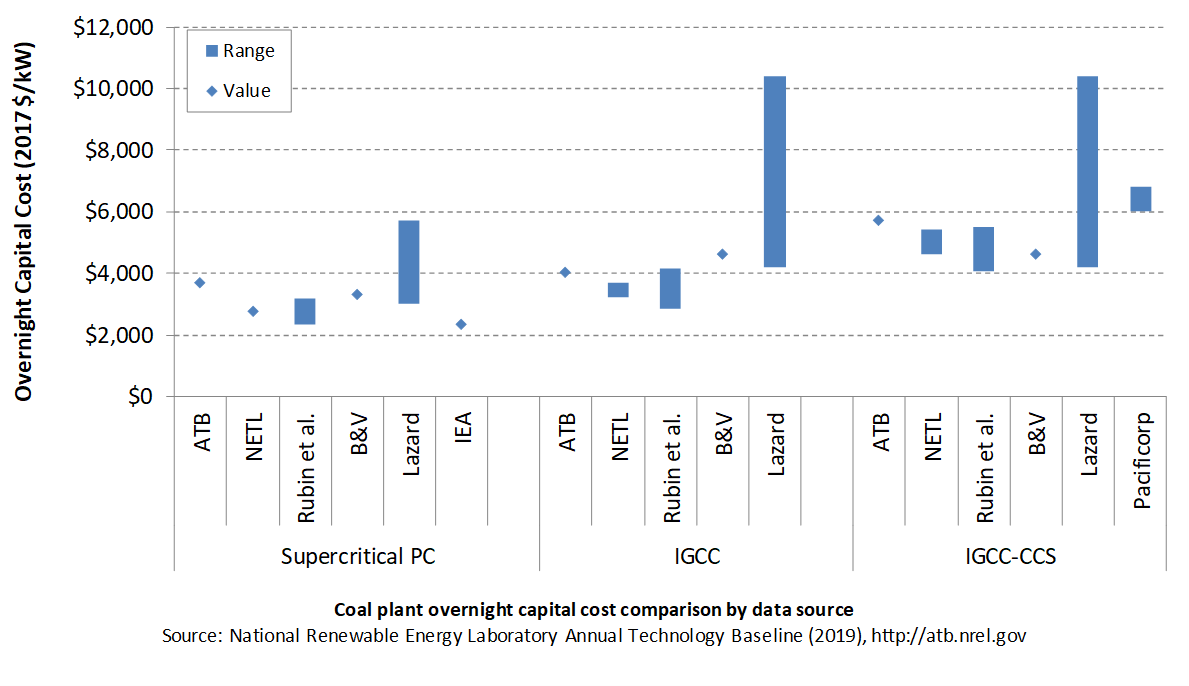
Lazard (2016) does not explicitly define its ranges with and without CCS; thus, the high end of their pulverized coal and IGCC ranges and the low end of their IGCC-CCS range are assumed to be the middle of the full reported range. All sources have been normalized to the same dollar year. Costs vary due to differences in system design (e.g., coal rank), methodology, and plant cost definitions. The coal capital costs include environmental controls to meet current federal regulations.
CAPEX Definition
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year.
For coal power plants, CAPEX equals interest during construction (ConFinFactor) times the overnight capital cost (OCC).
Overnight capital costs are modified from AEO2019 (EIA, 2019a). The EIA projections were adjusted by removing the material price index. The material price index accounts for projected changes in the price index for metals and metals products, and it is independent of the learning-based cost reductions applied in the EIA projections.
For the ATB, coal-CCS technology is ultra-supercritical pulverized coal technology fitted with CCS. Both 30% capture and 90% capture options are included for the coal-CCS technology. The CCS plant configuration includes only the cost of capturing and compressing the CO2. It does not include CO2 delivery and storage.
| Overnight Capital Cost ($/kW) | Construction Financing Factor (ConFinFactor) | CAPEX ($/kW) | |
| Coal-new: Ultra-supercritical pulverized coal with SO2 and NOx controls | $3,711 | 1.087 | $4,036 |
| Coal-IGCC: Integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) | $4,055 | 1.087 | $4,409 |
| Coal-CCS: Ultra-supercritical pulverized coal with carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) options (30% / 90% capture) | $5,180 / $5,728 | 1.087 | $5,633 / $6,229 |
CAPEX can be determined for a plant in a specific geographic location as follows:
Regional cost variations and geographically specific grid connection costs are not included in the ATB (CapRegMult = 1; GCC = 0). In the ATB, the input value is overnight capital cost (OCC) and details to calculate interest during construction (ConFinFactor).
In the ATB, CAPEX represents each type of coal plant with a unique value. Regional cost effects associated with labor rates, material costs, and other regional effects as defined by (EIA, 2016) expand the range of CAPEX. Unique land-based spur line costs based on distance and transmission line costs are not estimated. The following figure illustrates the ATB representative plant relative to the range of CAPEX including regional costs across the contiguous United States. The ATB representative plants are associated with a regional multiplier of 1.0.
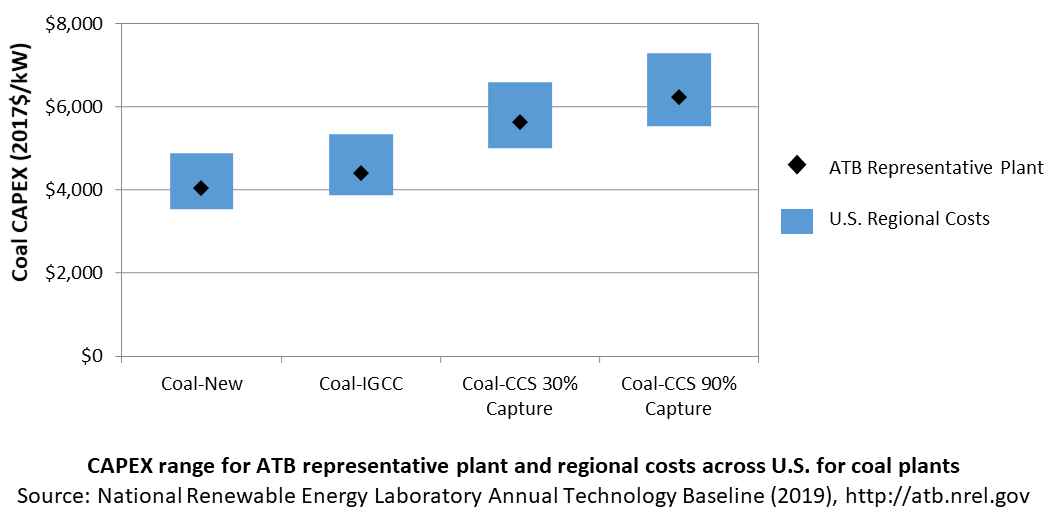
Operation and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
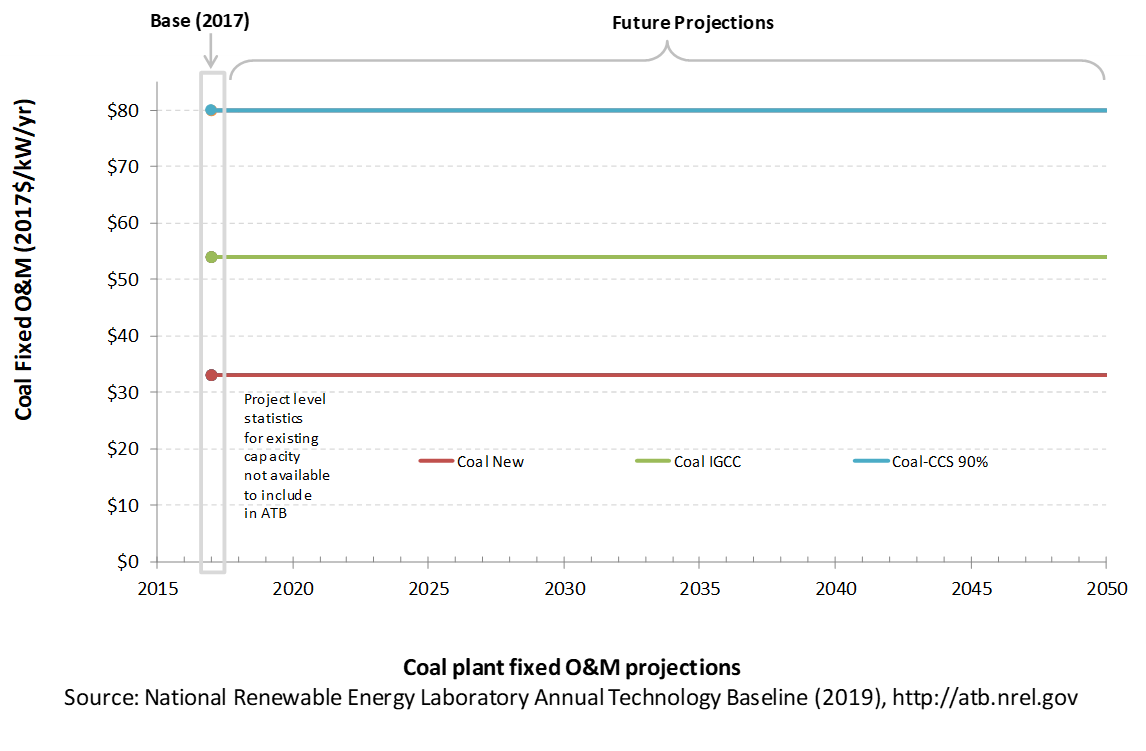
Coal power plant fixed and variable O&M costs are taken from table 8.2 of the AEO2019, and they are assumed to be constant over time.
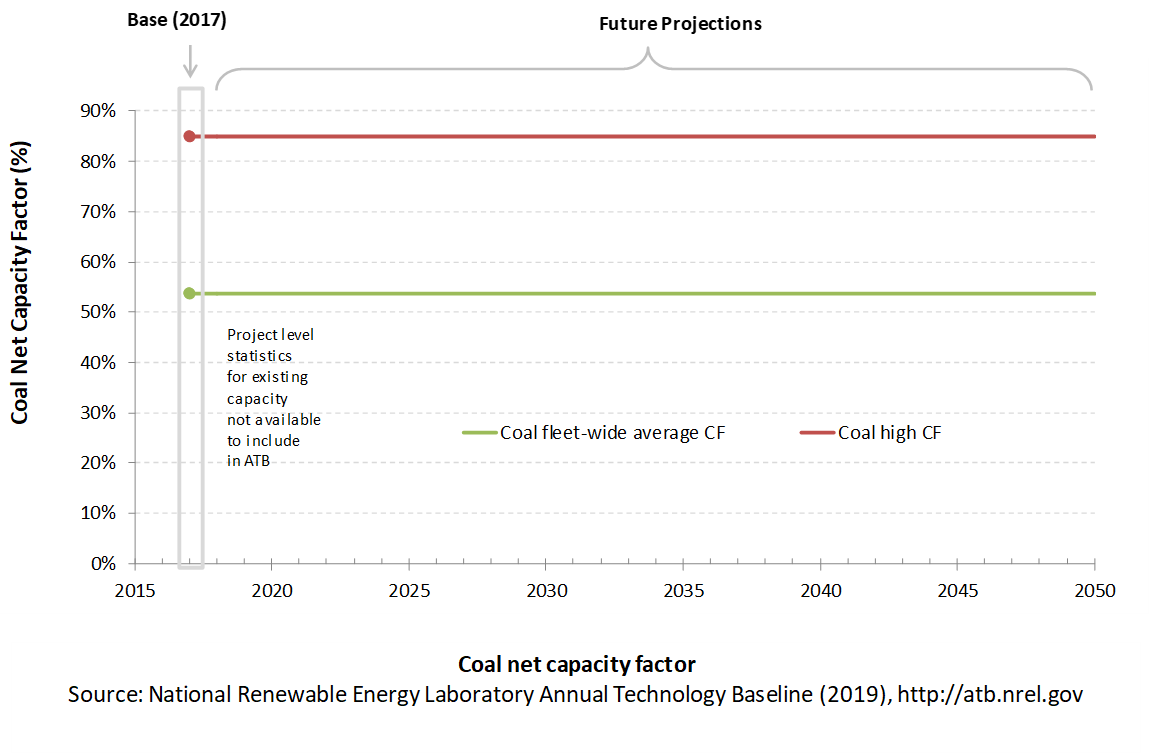
Capacity Factor: Expected Annual Average Energy Production Over Lifetime
The capacity factor represents the assumed annual energy production divided by the total possible annual energy production, assuming the plant operates at rated capacity for every hour of the year. For coal plants, the capacity factors are typically lower than their availability factors. Coal plant availability factors have a wide range depending on system design and maintenance schedules.
The capacity factor of dispatchable units is typically a function of the unit's marginal costs and local grid needs (e.g., need for voltage support or limits due to transmission congestion).
Coal power plants have typically been operated as baseload units, although that has changed in many locations due to low natural gas prices and increased penetration of variable renewable technologies. The average capacity factor used in the ATB is the fleet-wide average reported by EIA for 2017. The high capacity factor represents a new plant that would operate as a baseload unit. New coal plants would likely be more efficient than existing coal plants, and therefore would be more likely to be dispatched more often, resulting in capacity factors closer to the "high" level than the "average" level, but actual capacity factors will vary based on local grid conditions and needs.
Even though IGCC and coal with CCS have experienced limited deployment in the United States, it is expected that their performance characteristics would be similar to new coal power plants.
Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) Projections
Levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is a summary metric that combines the primary technology cost and performance parameters: CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor. It is included in the ATB for illustrative purposes. The ATB focuses on defining the primary cost and performance parameters for use in electric sector modeling or other analysis where more sophisticated comparisons among technologies are made. The LCOE accounts for the energy component of electric system planning and operation. The LCOE uses an annual average capacity factor when spreading costs over the anticipated energy generation. This annual capacity factor ignores specific operating behavior such as ramping, start-up, and shutdown that could be relevant for more detailed evaluations of generator cost and value. Electricity generation technologies have different capabilities to provide such services. For example, wind and PV are primarily energy service providers, while the other electricity generation technologies provide capacity and flexibility services in addition to energy. These capacity and flexibility services are difficult to value and depend strongly on the system in which a new generation plant is introduced. These services are represented in electric sector models such as the ReEDS model and corresponding analysis results such as the Standard Scenarios.
Biopower
The ATB includes both dedicated biopower cost options and a biomass cofired with coal option. The cost and performance characteristics of these plants are adapted from EIA data rather than derived from original analysis.
Capital Expenditures (CAPEX): Historical Trends, Current Estimates, and Future Projections
Biopower plant CAPEX is taken from the AEO2019 Reference Scenario (EIA, 2019a) with the adjustments discussed in the CAPEX definition section.
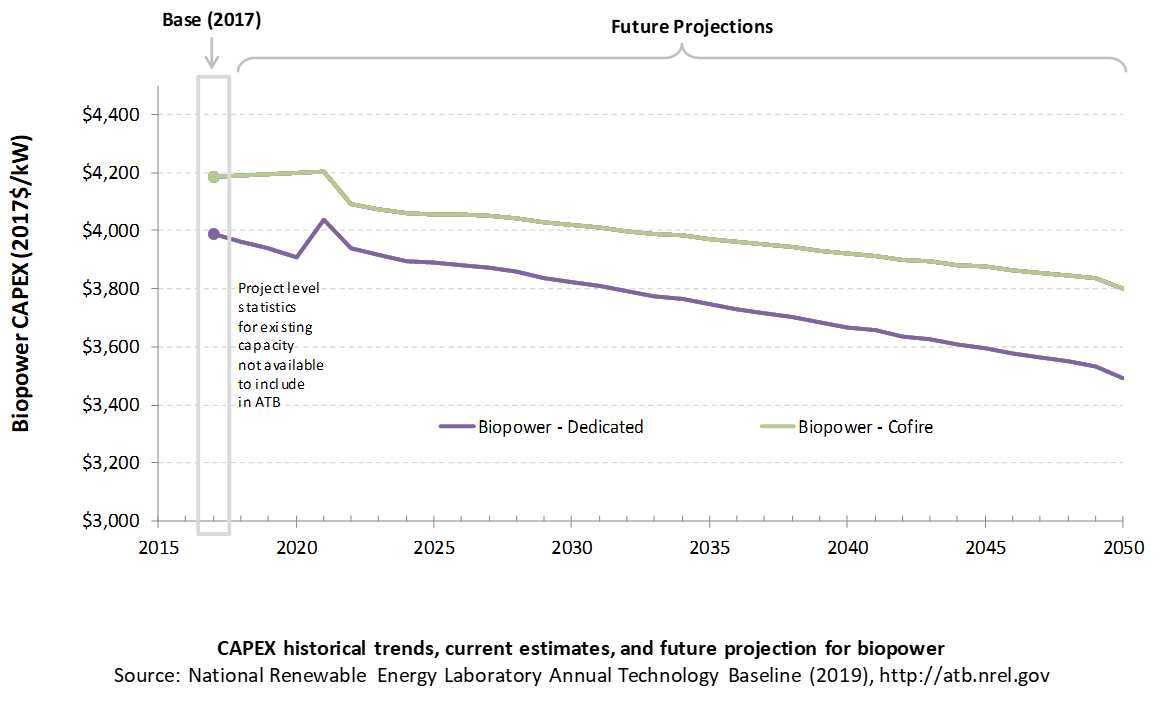
CAPEX Definition
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year.
Overnight capital costs are modified from AEO2019 (EIA, 2019a). The EIA projections were adjusted by removing the material price index. The material price index accounts for projected changes in the price index for metals and metals products, and it is independent of the learning-based cost reductions applied in the EIA projections.
Fuel costs are taken from the Billion Ton Update study (DOE et al., 2011).
| Overnight Capital Cost ($/kW) | Construction Financing Factor (ConFinFactor) | CAPEX ($/kW) | |
| Dedicated: Dedicated biopower plant | $3,827 | 1.042 | $3,990 |
| CofireOld: Pulverized coal with sulfur dioxide (SO2) scrubbers and biomass co-firing | $4,013 | 1.042 | $4,184 |
| CofireNew: Advanced supercritical coal with SO2 and NOx controls and biomass co-firing | $4,013 | 1.042 | $4,184 |
CAPEX can be determined for a plant in a specific geographic location as follows:
Regional cost variations and geographically specific grid connection costs are not included in the ATB (CapRegMult = 1; GCC = 0). In the ATB, the input value is overnight capital cost (OCC) and details to calculate interest during construction (ConFinFactor).
In the ATB, CAPEX represents each type of biopower plant with a unique value. Regional cost effects associated with labor rates, material costs, and other regional effects as defined by (EIA, 2016) expand the range of CAPEX. Unique land-based spur line costs based on distance and transmission line costs are not estimated. The following figure illustrates the ATB representative plant relative to the range of CAPEX including regional costs across the contiguous United States. The ATB representative plants are associated with a regional multiplier of 1.0.
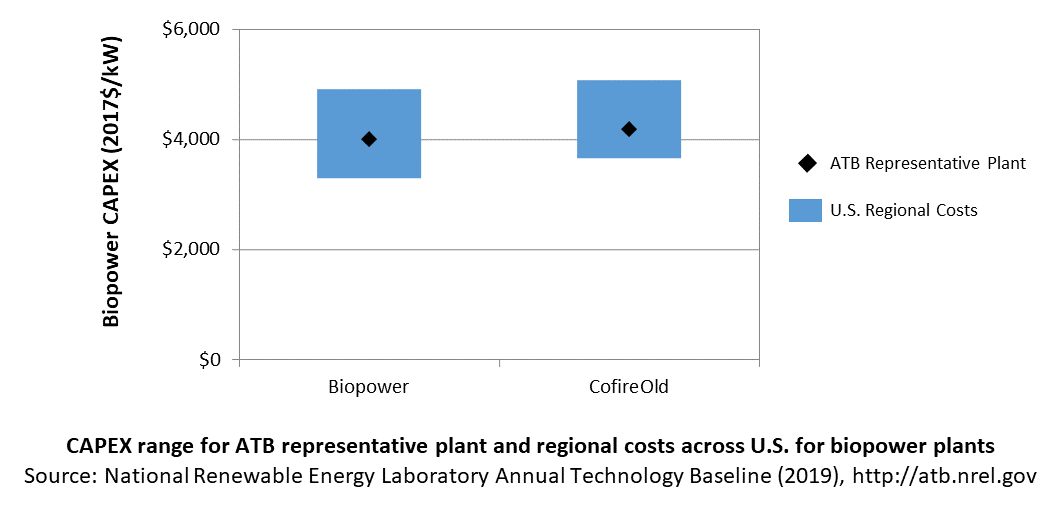
Operation and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
Biopower power plant fixed and variable O&M costs are taken from table 8.2 of the AEO2019, and they are assumed to be constant over time.
Capacity Factor: Expected Annual Average Energy Production Over Lifetime
The capacity factor represents the assumed annual energy production divided by the total possible annual energy production, assuming the plant operates at rated capacity for every hour of the year. For biopower plants, the capacity factors are typically lower than their availability factors. Biopower plant availability factors have a wide range depending on system design, fuel type and availability, and maintenance schedules.
Biopower plants are typically baseload plants with steady capacity factors. For the ATB, the biopower capacity factor is taken as the average capacity factor for biomass plants for 2017, as reported by EIA.
Biopower capacity factors are influenced by technology and feedstock supply, expected downtime, and energy losses.
Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) Projections
Levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is a summary metric that combines the primary technology cost and performance parameters: CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor. It is included in the ATB for illustrative purposes. The ATB focuses on defining the primary cost and performance parameters for use in electric sector modeling or other analysis where more sophisticated comparisons among technologies are made. The LCOE accounts for the energy component of electric system planning and operation. The LCOE uses an annual average capacity factor when spreading costs over the anticipated energy generation. This annual capacity factor ignores specific operating behavior such as ramping, start-up, and shutdown that could be relevant for more detailed evaluations of generator cost and value. Electricity generation technologies have different capabilities to provide such services. For example, wind and PV are primarily energy service providers, while the other electricity generation technologies provide capacity and flexibility services in addition to energy. These capacity and flexibility services are difficult to value and depend strongly on the system in which a new generation plant is introduced. These services are represented in electric sector models such as the ReEDS model and corresponding analysis results such as the Standard Scenarios.
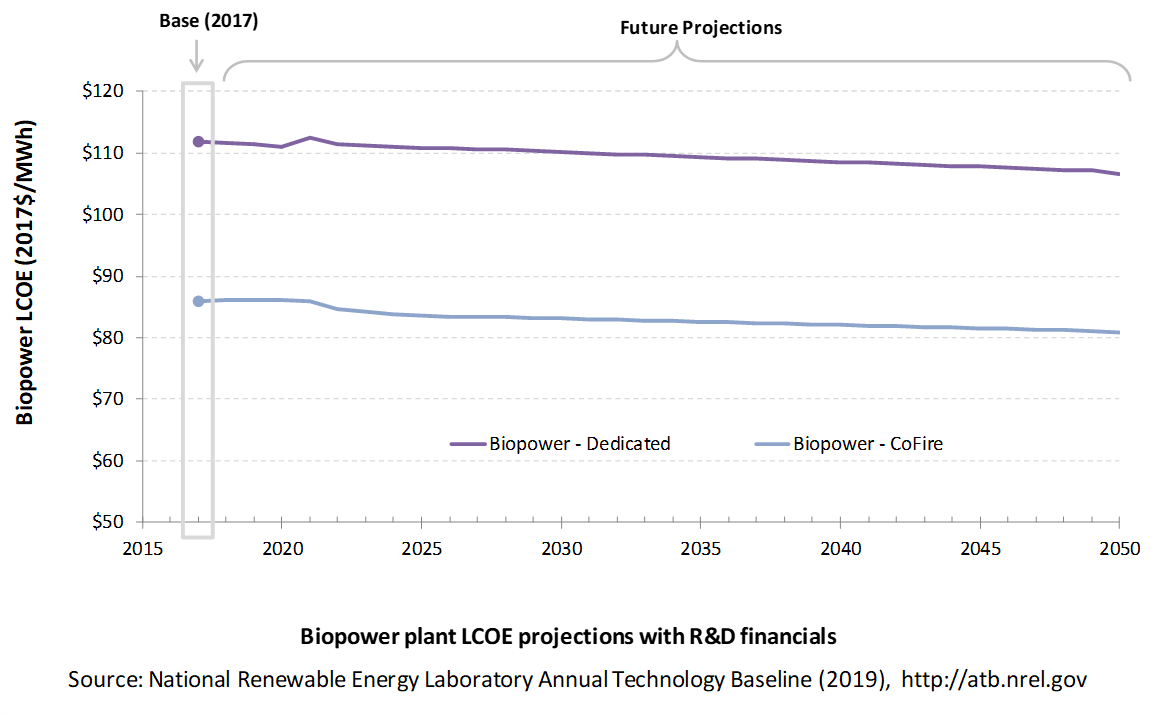
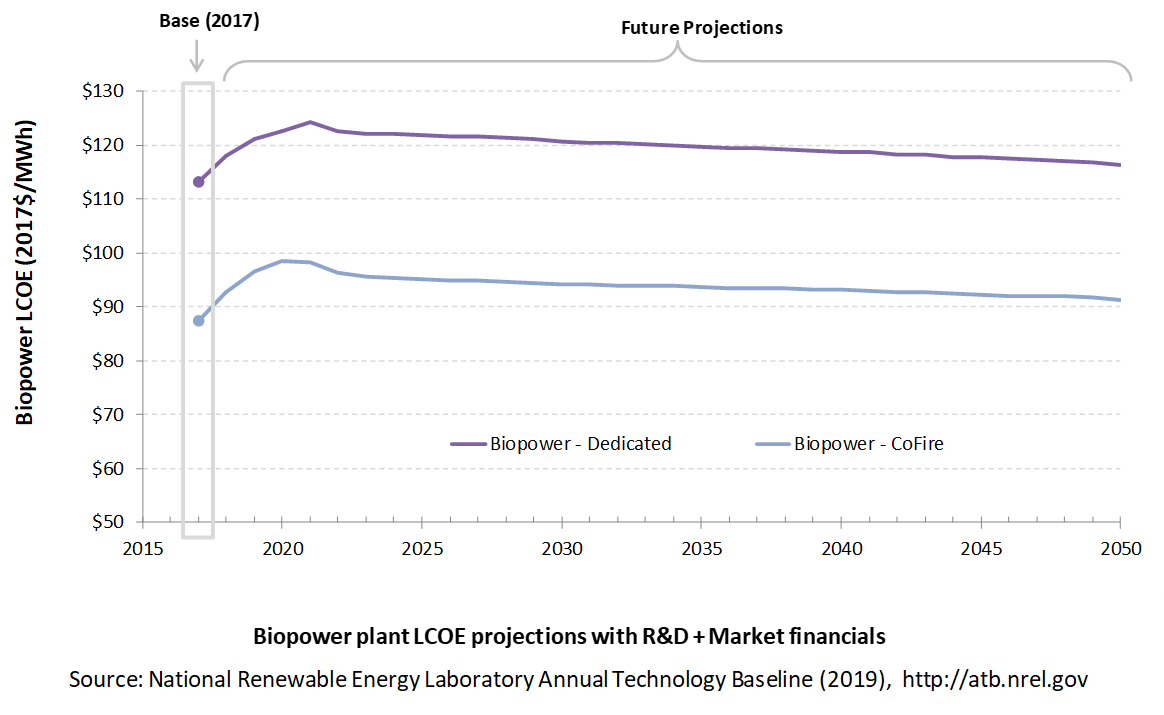
The following three figures illustrate LCOE, which includes the combined impact of CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor projections for biomass across the range of resources present in the contiguous United States. For the purposes of the ATB, the costs associated with technology and project risk in the U.S. market are represented in the financing costs but not in the upfront capital costs (e.g., developer fees and contingencies). An individual technology may receive more favorable financing terms outside the United States, due to less technology and project risk, caused by more project development experience (e.g., offshore wind in Europe) or more government or market guarantees. The R&D Only LCOE sensitivity cases present the range of LCOE based on financial conditions that are held constant over time unless R&D affects them, and they reflect different levels of technology risk. This case excludes effects of tax reform, tax credits, and changing interest rates over time. The R&D + Market LCOE case adds to these financial assumptions: (1) the changes over time consistent with projections in the Annual Energy Outlook and (2) the effects of tax reform and tax credits. Data for all the resource categories can be found in the ATB data spreadsheet; for simplicity, not all resource categories are shown in the figures.
R&D Only | R&D + Market
The LCOE of biopower plants is directly impacted by the differences in CAPEX (installed capacity costs) as well as by heat rate differences. For a given year, the LCOE assumes that the fuel prices from that year continue throughout the lifetime of the plant.
Regional variations will ultimately impact biomass feedstock costs, but these are not included in the ATB.
The projections do not include any cost of carbon.
Fuel costs are taken from the Billion Ton Update study (DOE et al., 2011).
To estimate LCOE, assumptions about the cost of capital to finance electricity generation projects are required, and the LCOE calculations are sensitive to these financial assumptions. Two project finance structures are used within the ATB:
- R&D Only Financial Assumptions: This sensitivity case allows technology-specific changes to debt interest rates, return on equity rates, and debt fraction to reflect effects of R&D on technological risk perception, but it holds background rates constant at 2017 values from AEO2019 (EIA, 2019a) and excludes effects of tax reform and tax credits. A constant cost recovery period-or period over which the initial capital investment is recovered-of 30 years is assumed for all technologies.
- R&D Only + Market Financial Assumptions: This sensitivity case retains the technology-specific changes to debt interest, return on equity rates, and debt fraction from the R&D Only case and adds in the variation over time consistent with AEO2019 (EIA, 2019a) as well as effects of tax reform and tax credits. As in the R&D Only case, a constant cost recovery period-or period over which the initial capital investment is recovered-of 30 years is assumed for all technologies. For a detailed discussion of these assumptions, see Project Finance Impact on LCOE.
The equations and variables used to estimate LCOE are defined on the Equations and Variables page. For illustration of the impact of changing financial structures such as WACC, see Project Finance Impact on LCOE. For LCOE estimates for the Constant, Mid, and Low technology cost scenarios for all technologies, see 2019 ATB Cost and Performance Summary.
References
The following references are specific to this page; for all references in this ATB, see References.Ardani, K., O'Shaughnessy, E., Fu, R., McClurg, C., Huneycutt, J., & Margolis, R. (2017). Installed Cost Benchmarks and Deployment Barriers for Residential Solar Photovoltaics with Energy Storage: Q1 2016 (No. NREL/TP-7A40-67474). Retrieved from National Renewable Energy Laboratory website: Installed Cost Benchmarks and Deployment Barriers for Residential Solar Photovoltaics with Energy Storage: Q1 2016
Augustine, Chad, Ho, J., & Blair, N. (2019). GeoVision Analysis Supporting Task Force Report: Electric Sector Potential to Penetration (No. NREL/ TP-6A20-71833). Retrieved from National Renewable Energy Laboratory website: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy19osti/71833.pdf
Augustine, Chad. (2016). Updates to Enhanced Geothermal System Resource Potential Estimate. GRC Transactions, 40, 673–677. Retrieved from http://pubs.geothermal-library.org/lib/grc/1032382.pdf
Black & Veatch. (2012). Cost and Performance Data for Power Generation Technologies. Retrieved from Black & Veatch Corporation website: https://www.bv.com/docs/reports-studies/nrel-cost-report.pdf
Cole, Wesley, & Frazier, A. Will. (2019). Cost Projections for Utility-Scale Battery Storage (No. NREL/TP-6A20-73222). Retrieved from National Renewable Energy Laboratory website: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy19osti/73222.pdf
DOE. (2011). U.S. Billion-Ton Update: Biomass Supply for a Bioenergy and Bioproducts Industry (No. ORNL/TM-2011/224). https://doi.org/10.2172/1023318
DOE. (2019). GeoVision: Harnessing the Heat Beneath Our Feet (No. DOE/EE-1306). Retrieved from U.S. Department of Energy website: https://www.energy.gov/eere/geothermal/geovision
EIA. (2015). Annual Energy Outlook 2015 with Projections to 2040 (No. AEO2015). Retrieved from U.S. Energy Information Administration website: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/pdf/0383(2015).pdf
EIA. (2016b). Capital Cost Estimates for Utility Scale Electricity Generating Plants. Retrieved from U.S. Energy Information Administration website: https://www.eia.gov/analysis/studies/powerplants/capitalcost/pdf/capcost_assumption.pdf
EIA. (2019a). Annual Energy Outlook 2019 with Projections to 2050. Retrieved from U.S. Energy Information Administration website: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/pdf/AEO2019.pdf
EIA. (2019b, January). Table 6.7.B Capacity Factors for Utility Scale Generators Not Primarily Using Fossil Fuels. Retrieved April 22, 2019, from https://www.eia.gov/electricity/monthly/epm_table_grapher.php?t=epmt_6_07_b
Fu, R., Remo, T. W., & Margolis, R. M. (2018). 2018 U.S. Utility-Scale Photovoltaics-Plus-Energy Storage System Costs Benchmark (No. NREL/TP-6A20-71714). https://doi.org/10.2172/1483474
Lazard. (2016). Lazard's Levelized Cost of Energy Analysis: Version 10.0. Retrieved from Lazard website: https://www.lazard.com/media/438038/levelized-cost-of-energy-v100.pdf
Lopez, A., Roberts, B., Heimiller, D., Blair, N., & Porro, G. (2012). U.S. Renewable Energy Technical Potentials: A GIS-Based Analysis (Technical Report No. NREL/TP-6A20-51946). https://doi.org/10.2172/1219777
Mines, G. (2013, April). Geothermal Electricity Technology Evaluation Model (GETEM). Presented at the Geothermal Technologies Office 2013 Peer Review, Washington, D.C. Retrieved from https://energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2014/02/f7/mines_getem_peer2013.pdf
Roberts, B. J. (2009). Geothermal Resource of the United States: Locations of Identified Hydrothermal Sites and Favorability of Deep Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS). Retrieved from https://www.nrel.gov/gis/images/geothermal_resource2009-final.jpg
Rubin, E. S., Davison, J. E., & Herzog, H. J. (2015). The Cost of CO2 Capture and Storage. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 40, 378–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.05.018
Tester, J. W., & et al. (2006). The Future of Geothermal Energy: Impact of Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) on the United States in the 21st Century. Cambridge, MA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
USGS. (2008). Assessment of Moderate- and High-Temperature Geothermal Resources of the United States (No. Fact Sheet 2008-3082). Retrieved from U.S. Geological Survey website: https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2008/3082/pdf/fs2008-3082.pdf
Zoelle, A., Keairns, D., Pinkerton, L. L., Turner, M. J., Woods, M., Kuehn, N., … Chou, V. (2015). Cost and Performance Baseline for Fossil Energy Plants Volume 1a: Bituminous Coal (PC) and Natural Gas to Electricity Revision 3 (No. DOE/NETL-2015/1723). https://doi.org/10.2172/1480987