Annual Technology Baseline 2017
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
Recommended Citation:
NREL (National Renewable Energy Laboratory). 2017. 2017 Annual Technology Baseline. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. http://atb.nrel.gov/.
Please consult Guidelines for Using ATB Data:
https://atb.nrel.gov/electricity/user-guidance.html
Utility-Scale PV Power Plants
Representative Technology
Utility-scale PV systems in the ATB are representative of one-axis tracking systems with performance characteristics in line with a 1.1 DC-to-AC ratio - or inverter loading ratio (ILR) - and pricing characteristics in line with a 1.2 DC-to-AC ratio (Fu et al. 2016). PV system performance characteristics were designed in the ReEDS model at a time when PV system ILRs were lower than they are in current system designs; pricing in the 2017 ATB incorporates more up-to-date system designs and therefore assumes a higher ILR.
Resource Potential
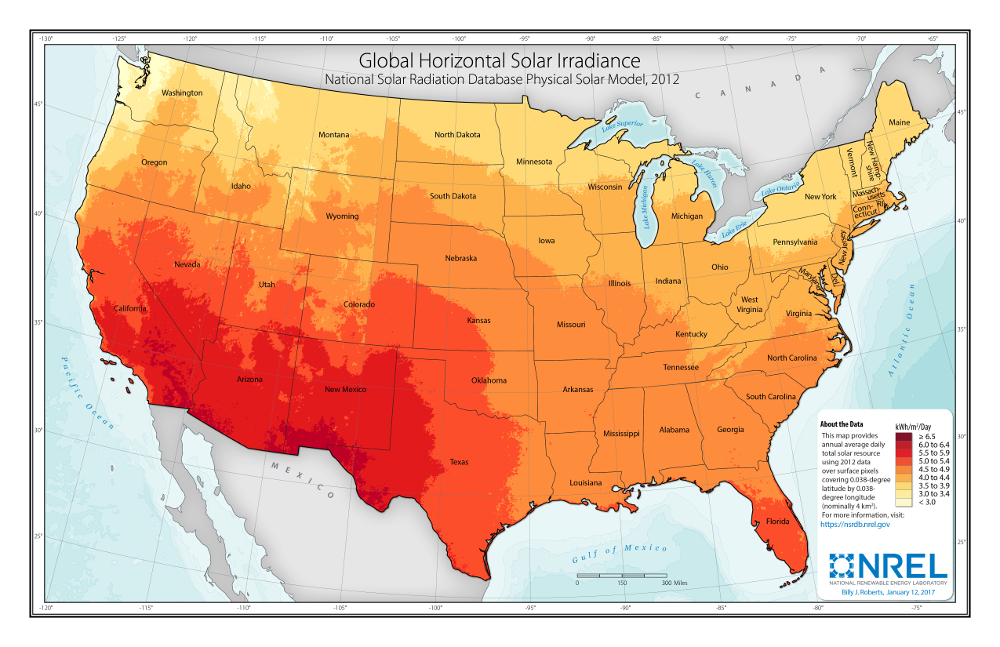
Solar resources across the United States are mostly good to excellent at about 1,000-2,500 kWh/m2/year. The Southwest is at the top of this range, while Alaska and part of Washington are at the low end. The range for the contiguous United States is about 1,350-2,500 kWh/m2/year. Nationwide, solar resource levels vary by about a factor of two.
The total U.S. land area suitable for PV is significant and will not limit PV deployment. One estimate (Denholm and Margolis 2008) suggests the land area required to supply all end-use electricity in the United States using PV is about 5,500,000 hectares (ha) (13,600,000 acres), which is equivalent to 0.6% of the country's land area or about 22% of the "urban area" footprint (this calculation is based on deployment/land in all 50 states).
Renewable energy technical potential, as defined by Lopez et al. (2012), represents the achievable energy generation of a particular technology given system performance, topographic limitations, and environmental and land-use constraints. The primary benefit of assessing technical potential is that it establishes an upper-boundary estimate of development potential. It is important to understand that there are multiple types of potential - resource, technical, economic, and market (Lopez et al. 2012; NREL, "Renewable Energy Technical Potential").
Base Year and Future Year Projections Overview
The Base Year estimates rely on modeled CAPEX and O&M estimates benchmarked with industry and historical data. Capacity factor is estimated based on hours of sunlight at latitude for all geographic locations in the United States. The ATB presents capacity factor estimates that encompass a range associated with low, mid, and high levels across the United States.
Future year projections are derived from analysis of published projections of PV CAPEX and bottom-up engineering analysis of O&M costs. Three different projections were developed for scenario modeling as bounding levels:
- High cost: no change in CAPEX, O&M, or capacity factor from 2016 to 2050; consistent across all renewable energy technologies in the ATB
- Mid cost: based on the median of literature projections of future CAPEX; O&M technology pathway analysis
- Low Cost: based on low bound of literature projections of future CAPEX; O&M technology pathway analysis.
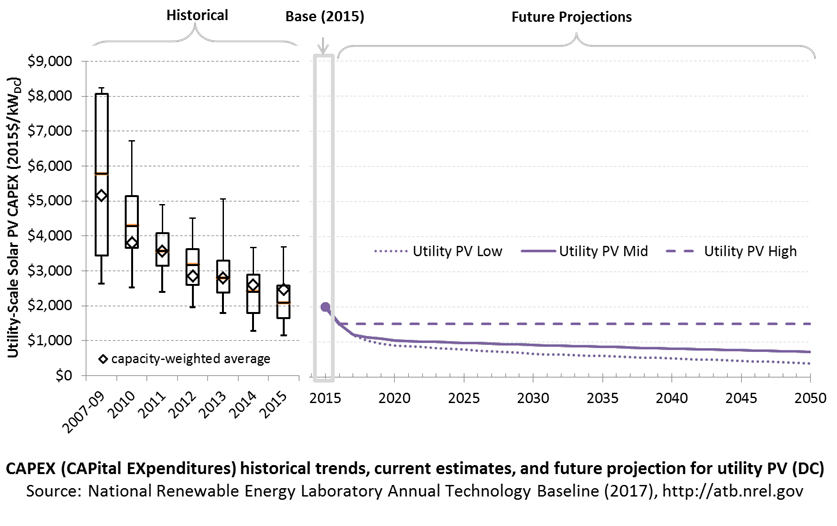
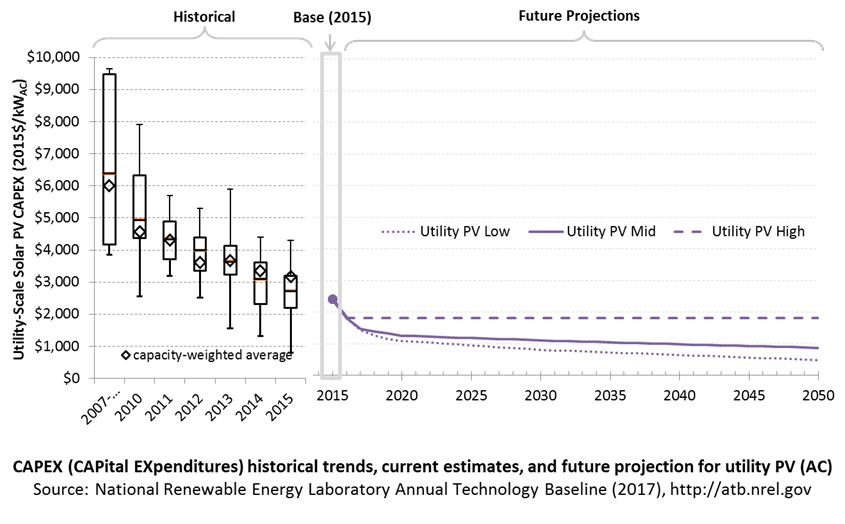
CAPital EXpenditures (CAPEX): Historical Trends, Current Estimates, and Future Projections
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year. These expenditures include the hardware, the balance of system (e.g., site preparation, installation, and electrical infrastructure), and financial costs (e.g., development costs, onsite electrical equipment, and interest during construction) and are detailed in CAPEX Definition. In the ATB, CAPEX reflects typical plants and does not include differences in regional costs associated with labor or materials. The range of CAPEX demonstrates variation with resource in the contiguous United States.
The following figures show the Base Year estimate and future year projections for CAPEX costs in terms of $/kWDC or $/kWAC. Three cost reduction scenarios are represented: High, Mid, and Low. Historical data from utility-scale PV plants installed in the United States are shown for comparison to the ATB Base Year estimates. The estimate for a given year represents CAPEX of a new plant that reaches commercial operation in that year.
The PV industry typically refers to PV CAPEX in terms of $/kWDC based on the aggregated module capacity. The electric utility industry typically refers to PV CAPEX in terms of $/kWAC based on the aggregated inverter capacity. See Solar PV AC-DC Translation for details. The figures illustrate the CAPEX historical trends, current estimates, and future projections in terms of $/kWDC or $/kWAC assuming an inverter loading ratio of 1.2.
Recent Trends
Reported historical utility-scale PV plant CAPEX (Bolinger and Seel 2016) is shown in box-and-whiskers format for comparison to the ATB current CAPEX estimates and future projections. Bolinger and Seel (2016) provide statistical representation of CAPEX for 89% of all utility-scale PV capacity.
PV pricing and capacities are quoted in kWDC (i.e., module rated capacity) unlike other generation technologies, which are quoted in kWAC. For PV, this would correspond to the combined rated capacity of all inverters. This is done because kWDC is the unit that the majority of the PV industry uses. Although costs are reported in kWDC, the total CAPEX includes the cost of the inverter, which has a capacity measured in kWAC.
CAPEX estimates for 2015 reflect continued rapid decline supported by analysis of recent power purchase agreement pricing (Bolinger and Seel 2016) for projects that will become operational in 2015 and beyond.
Base Year Estimates
For illustration in the ATB, a representative utility-scale PV plant is shown. Although the PV technologies vary, typical plant costs are represented with a single estimate because the CAPEX does not vary with solar resource.
Although the technology market share may shift over time with new developments, the typical plant cost is represented with the projections above.
A system price of $2.01/WDC in 2015 represents the median price of a utility-scale PV system installed in 2015 as reported in Bolinger and Seel (2016) and adjusted to remove regional cost multipliers based on geographic location of projects installed in 2015. The $1.51/WDC price in 2016 is based on modeled pricing for one-axis tracking systems quoted in Q1 2016 as reported in Fu et al. (2016) and adjusted for inflation. These figures are in line with other estimated system prices reported in Feldman et al. (2016).
The Base Year CAPEX estimates should tend toward the low end of reported pricing because no regional impacts, time-lagged system prices, or spur line costs are included. These effects are represented in the historical market data.
For example, in 2014, the reported capacity-weighted average system price was higher than 80% of system prices in 2014 due to very large systems, with multi-year construction schedules, installed in that year. Developers of these large systems negotiated contracts and installed portions of their systems when module and other costs were higher.
Future Year Projections
Projections of future utility-scale PV plant CAPEX are based on 14 system price projections from 8 separate institutions with short-term projections made in the past six months and long-term projections made in the last three years. We adjusted the "min," "median," and "max" analyst forecasts in a few different ways. All 2015 pricing is based on the median utility-scale system price as reported in Utility-Scale Solar 2015 (Bolinger and Seel 2016) and adjusted by the ReEDS state-level capital cost multipliers to remove geographic price distortions from 2015 reported pricing. All 2016 pricing is based on the bottom-up benchmark analysis reported in U.S. Solar Photovoltaic System Cost Benchmark Q1 2016 (adjusted for inflation) (Fu et al. 2016). These figures are in line with other estimated system prices reported in Feldman et al. (2016).
We adjusted the Mid and Low projections for 2017-2050 to remove distortions caused by the combination of forecasts with different time horizons and based on internal judgment of price trends. The High projection case is kept constant at the 2016 CAPEX value, assuming no improvements beyond 2016.
The largest annual reductions in CAPEX for the Mid and Low projections occur from 2015 to 2017, dropping 25% from 2015 to 2016 and another 19%-22% from 2016 to 2017. While reported CAPEX values have not been collected for all systems built in 2016 and 2017, CAPEX information collected from Annual Reports of Major Electric Utilities from the Federal Regulatory Commission (FERC Form 1) from nine major utilities found a 22% reduction in CAPEX from 2015 to 2016, falling to $1.32/W, which is well below reported CAPEX in the ATB. (FERC Form 1 collected from the FERC Online elibrary for the following utilities: Arizona Public Service, Florida Power & Light, Duke Energy Progressive, Georgia Power, Indiana Michigan Power Company, Kentucky Utilities, Pacific Gas & Electric, Public Service of New Mexico, and Southern California Edison.) The ATB values in 2017 are based on analysts' forecasts. Additionally, initially reported pricing for utility-scale power purchase agreements (PPAs) for utility-scale systems placed in service in that year fell 33% from 2015 to 2016; the ATB LCOE reduction over the same period is 23%.
Detailed description of the methodology for developing Future Year Projections is found in Projections Methodology.
Technology innovations that could impact future CAPEX costs are summarized in LCOE Projections.
CAPEX Definition
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year.
For the ATB—and based on EIA (2016a) and the NREL Solar PV Cost Model (Fu et al. 2016) - the utility-scale solar PV plant envelope is defined to include:
- Hardware
- Module supply
- Power electronics, including inverters
- Racking
- Foundation
- AC and DC wiring materials and installation
- Electrical infrastructure, such as transformers, switchgear, and electrical system connecting modules to each other and to the control center
- Balance of system
- Land acquisition, site preparation, installation of underground utilities, access roads, fencing, and buildings for operations and maintenance
- Project indirect costs, including costs related to engineering, distributable labor and materials, construction management start up and commissioning, and contractor overhead costs, fees, and profit.
- Financial Costs
- Owner's costs, such as development costs, preliminary feasibility and engineering studies, environmental studies and permitting, legal fees, insurance costs, and property taxes during construction.
- Electrical interconnection, including onsite electrical equipment (e.g., switchyard), a nominal-distance spur line (<1 mile), and necessary upgrades at a transmission substation; distance-based spur line cost (GCC) not included in the ATB
- Interest during construction estimated based on six-month duration accumulated 100% at half-year intervals and an 8% interest rate (ConFinFactor).
CAPEX can be determined for a plant in a specific geographic location as follows:
CAPEX = ConFinFactor*(OCC*CapRegMult+GCC).
(See the Financial Definitions tab in the ATB data spreadsheet.)
Regional cost variations and geographically specific grid connection costs are not included in the ATB (CapRegMult = 1; GCC = 0). In the ATB, the input value is overnight capital cost (OCC) and details to calculate interest during construction (ConFinFactor).
In the ATB, CAPEX represents a typical one-axis utility-scale PV plant and does not vary with resource. The difference in cost between tracking and non-tracking systems has been reduced greatly in the United States. Regional cost effects associated with labor rates, material costs, and other regional effects as defined by EIA (2016a) expand the range of CAPEX. Unique land-based spur line costs based on distance and transmission line costs for potential utility-PV plant locations expand the range of CAPEX even further. The following figure illustrates the ATB representative plant relative to the range of CAPEX including regional costs across the contiguous United States. The ATB representative plants are associated with a regional multiplier of 1.0.
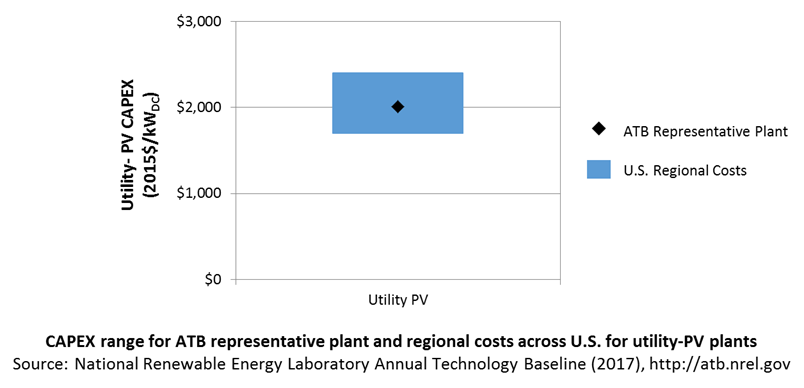
Standard Scenarios Model Results
ATB CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor assumptions for Base Year and future projections through 2050 for High, Mid, and Low projections are used to develop the NREL Standard Scenarios using the ReEDS model. See ATB and ATB and Standard Scenarios.
CAPEX in the ATB does not represent regional variants (CapRegMult) associated with labor rates, material costs, etc., but the ReEDS model does include 134 regional multipliers (EIA 2016a).
CAPEX in the ATB does not include a geographically determined spur line (GCC) from plant to transmission grid, but the ReEDS model calculates a unique value for each potential PV plant.
Operation and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
Operations and maintenance (O&M) costs represent the annual fixed expenditures required to operate and maintain a solar PV plant over its technical lifetime of 30 years (the distinction between economic life and technical life is described here), including:
- Insurance, property taxes, site security, legal and administrative fees, and other fixed costs
- Present value, annualized large component replacement costs over technical life (e.g., inverters at 15 years)
- Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance of solar PV plants, transformers, etc. over the technical lifetime of the plant (e.g., general maintenance, including cleaning and vegetation removal)
The following figure shows the Base Year estimate and future year projections for fixed O&M (FOM) costs. Three cost reduction scenarios are represented. The estimate for a given year represents annual average FOM costs expected over the technical lifetime of a new plant that reaches commercial operation in that year.
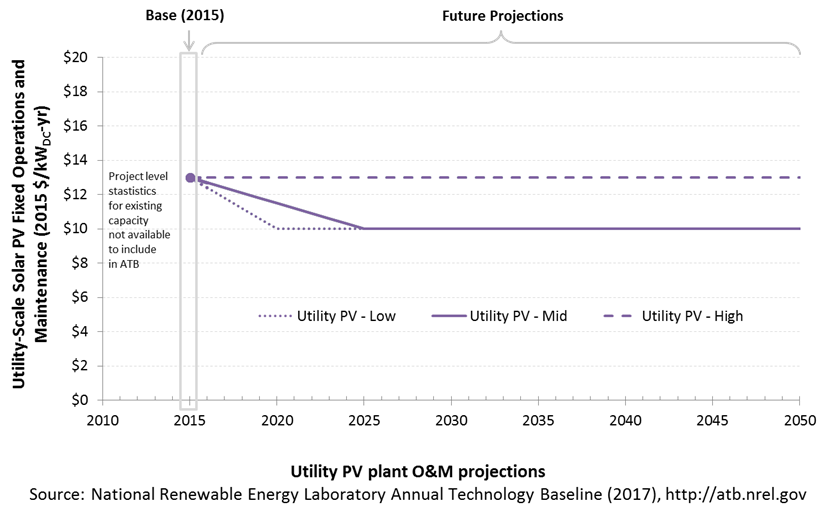
Base Year Estimates
FOM of $13/kWDC-yr is based on Bolinger and Seel (2016 ), who state that "average O&M costs for the cumulative set of PV plants within this sample have steadily declined from about $31/kWAC-yr (or $19/MWh) in 2011 to about $16/kWAC-yr ($7/MWh) in 2015." AC was converted into DC by dividing by 1.2. A wide range in reported prices exists in the market, in part depending on the maintenance practices that exist for a particular system. These cost categories include asset management (including compliance and reporting for incentive payments), different insurance products, site security, cleaning, vegetation removal, and failure of components. Not all these practices are performed for each system; additionally, some factors are dependent on the quality of the parts and construction. NREL analysts estimate O&M costs can range between $0 and $40/kWDC-yr.
Future Year Projections
Future FOM is assumed to decline to $10/kWDC-yr by 2020 in the Low cost case and by 2025 in the Mid cost case through improvements in system operation and more durable, better performing capital equipment, as per Woodhouse et al. 2016.
A detailed description of the methodology for developing future year projections is found in Projections Methodology.
Technology innovations that could impact future O&M costs are summarized in LCOE Projections.
Capacity Factor: Expected Annual Average Energy Production Over Lifetime
The capacity factor represents the expected annual average energy production divided by the annual energy production, assuming the plant operates at rated capacity for every hour of the year. It is intended to represent a long-term average over the technical lifetime of the plant (the distinction between economic life and technical life is described here). It does not represent interannual variation in energy production. Future year estimates represent the estimated annual average capacity factor over the technical lifetime of a new plant installed in a given year.
Other technologies' capacity factors are represented in exclusively AC units; however, because PV pricing in this ATB documentation is represented in $/kWDC, PV system capacity is a DC rating. The PV capacity factor is the ratio of annual average energy production (kWhAC) to annual energy production assuming the plant operates at rated DC capacity for every hour of the year. For more information, see Solar PV AC-DC Translation.
The capacity factor is influenced by the hourly solar profile, technology (e.g., thin-film versus crystalline silicon), axis type (e.g., none, one, or two), expected downtime, and inverter losses to transform from DC to AC power. The DC-AC ratio is a design choice that influences the capacity factor. PV plant capacity factor incorporates an assumed degradation rate of 0.5%/year (Jordan and Kurtz 2013) in the annual average calculation.
The following figure shows a range of capacity factors based on variation in solar resource in the contiguous United States. The range of the Base Year estimates illustrate the effect of locating a utility-scale PV plant in places with lower or higher solar irradiance. These values are the maximum, median, and minimum values for all geographic locations in the United States as implemented in the ReEDS model (Eurek et al. 2017 ). Future projections for High, Mid, and Low cost scenarios are unchanged from the Base Year. Technology improvements are focused on CAPEX and O&M cost elements.
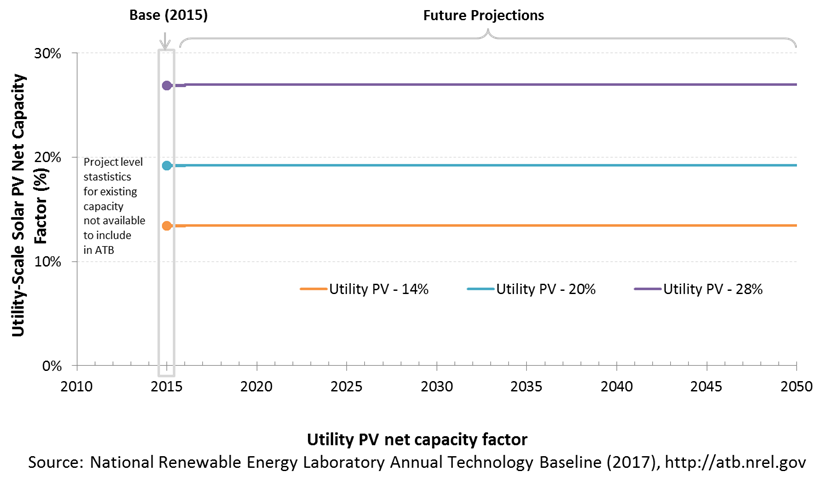
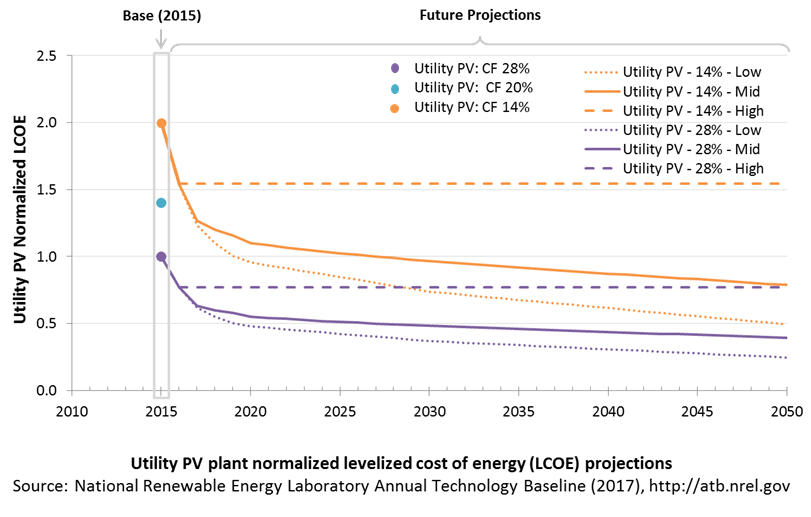
PV system inverters, which convert DC energy/power to AC energy/power, have AC capacity ratings; therefore, the capacity of a PV system is rated in MWAC, or the aggregation of all inverters' rated capacities, or MWDC, or the aggregation of all modules' rated capacities. The capacity factor calculation uses a system's rated capacity, and therefore, capacity factor can be represented using exclusively AC units or using AC units for electricity (the numerator) and DC units for capacity (the denominator). Both capacity factors will result in the same LCOE as long as the other variables use the same capacity rating (e.g., CAPEX in terms of $/kWDC). PV systems' DC ratings are typically higher than their AC ratings; therefore, the capacity factor calculated using a DC capacity rating has a higher denominator. In the ATB, we use capacity factors of 14%, 20%, and 28% for the first year of a PV project and adjust the values to reflect an average capacity factor for the lifetime of a project, calculated with MWDC, assuming 0.5% module capacity degradation per year. The adjusted average capacity factor values used in the ATB are 13.5%, 19.2%, and 26.9%. These numbers would change to approximately 14.8%, 21.2%, and 29.6% if the ATB used MWAC. The following figure illustrates capacity factor - both DC and AC - for a range of inverter loading ratios. The ATB capacity factor assumptions are based on ILR = 1.1.
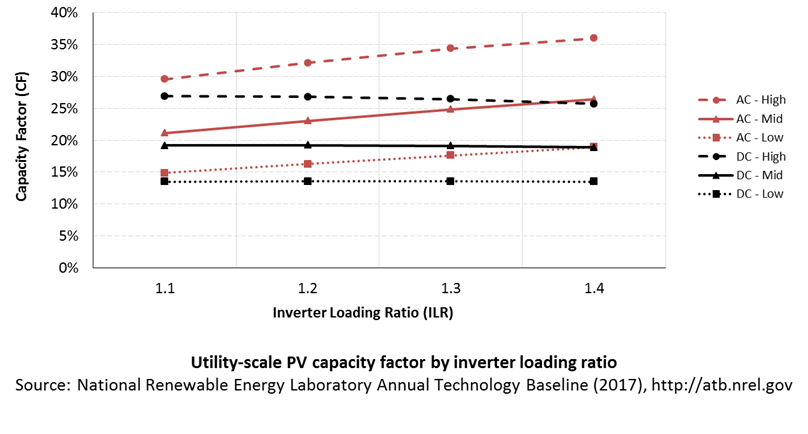
Recent Trends
At the end of 2015, the capacity-weighted average AC capacity factor for all U.S. projects installed at the time was 27.6% (including fixed-tilt systems), but individual project-level capacity factors exhibited a wide range (15.1%–35.7%).
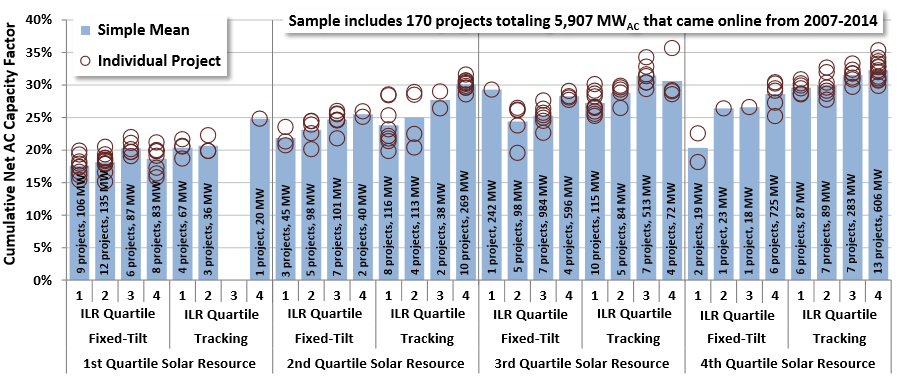
The capacity-weighted average capacity factor was more closely in line with the higher end of the range because 88% of the installed capacity was in the southwestern United States or California, where the average capacity factor was 30.2% for one-axis systems and 25.6% for fixed-tilt systems (Bolinger and Seel 2016). The upper and lower capacity factor values in the ATB are conservative due to the lower DC-to-AC ratio.
Base Year Estimates
For illustration in the ATB, a range of capacity factors associated with the range of latitude in the contiguous United States is shown.
Over time, PV plant output is reduced. This degradation (at 0.5%) is accounted for in ATB estimates of capacity factor. The ATB capacity factor estimates represent estimated annual average energy production over the 20-year economic life of the plant (the distinction between economic life and technical life is described here).
Given the historical reported capacity factors by systems installed in the United States and the potential for technological improvements that can improve the solar PV plant capacity factors (e.g., less reflectivity and improved low-light performance), these values likely represent a conservative estimate of system production. Part of this is due to differences in inverter loading ratios (also called DC-to-AC ratio), which can increase production but also increases cost ($/WDC). In 2015, the cumulative PV capacity factors for low-, mid-, and high-insolation regions, for tracking systems with a mid-level inverter loading ratio (1.19:1.25) were 20.7%, 26.7%, and 30.0% respectively (in WAC) (Bolinger and Seel 2016), which is comparable to or significantly higher than the 14.8%, 21.2%, and 29.6% (in WAC) used in the ATB (13.5%, 19.2%, and 26.9% in WDC). Currently reported capacity factors for deployed systems are, on average, reflective of capacity factors for relatively new plants.
These capacity factors are for a one-axis tracking system with a DC-to-AC ratio of 1.1.
Future Year Projections
Projections of capacity factors for plants installed in future years are unchanged from the Base Year. Solar PV plants have very little downtime, inverter efficiency is already optimized, and tracking is already assumed. That said, there is potential for future increases in capacity factors through technological improvements such as less panel reflectivity, lower degradation rates, and improved performance in low-light conditions.
Standard Scenarios Model Results
ATB CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor assumptions for the Base Year and future projections through 2050 for High, Mid, and Low projections are used to develop the NREL Standard Scenarios using the ReEDS model. See ATB and Standard Scenarios.
The ReEDS model output capacity factors for wind and solar PV can be lower than input capacity factors due to endogenously estimated curtailments determined by system operation.
Plant Cost and Performance Projections Methodology
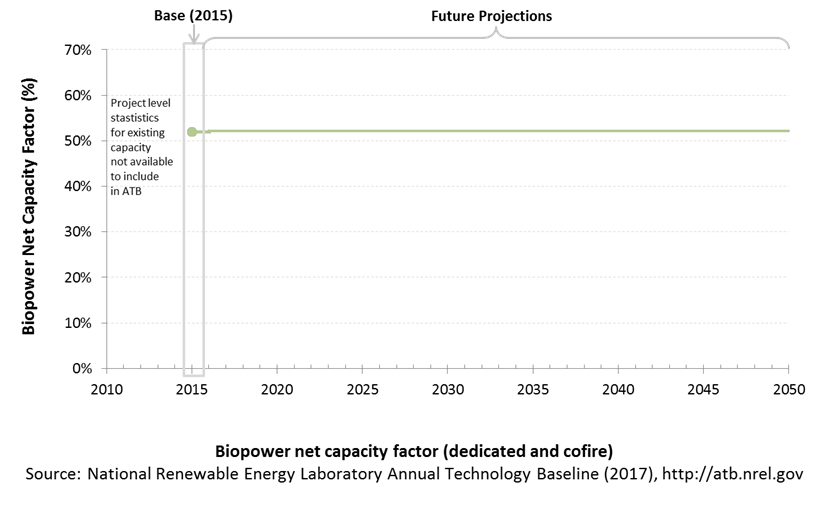
The capacity factor represents the assumed annual energy production divided by the total possible annual energy production, assuming the plant operates at rated capacity for every hour of the year. For biopower plants, the capacity factors are typically lower than their availability factors. Biopower plant availability factors have a wide range depending on system design, fuel type and availability, and maintenance schedules.
Biopower plants are typically baseload plants with steady capacity factors. For the ATB, the biopower capacity factor is taken as the average capacity factor for biomass plants for 2015, as reported by EIA.
Biopower capacity factors are influenced by technology and feedstock supply, expected downtime, and energy losses.
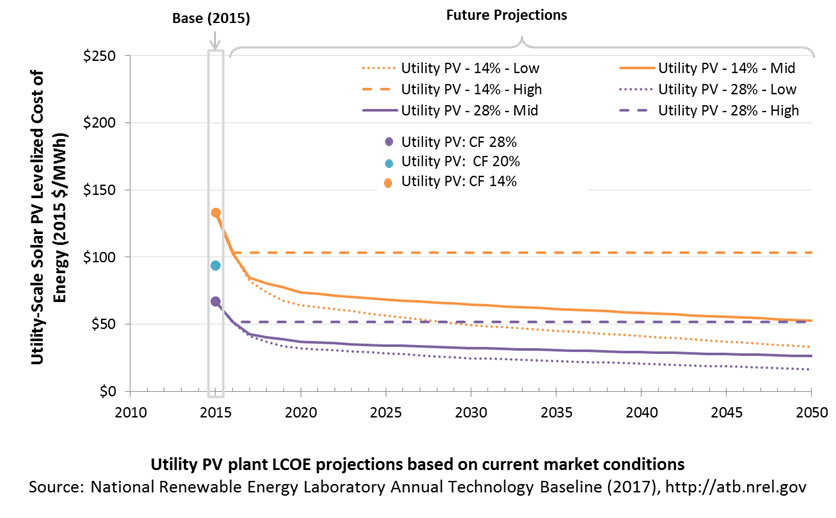
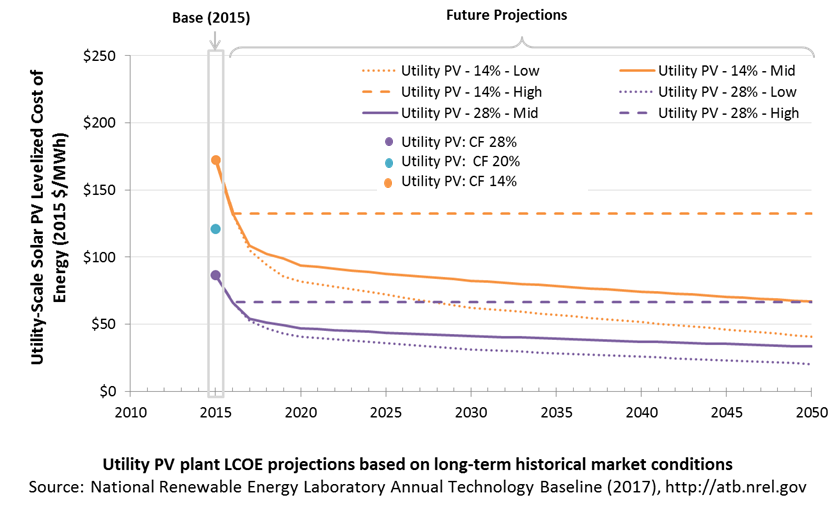
Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) Projections
Levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is a simple metric that combines the primary technology cost and performance parameters, CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor. It is included in the ATB for illustrative purposes. The focus of the ATB is to define the primary cost and performance parameters for use in electric sector modeling or other analysis where more sophisticated comparisons among technologies are made. LCOE captures the energy component of electric system planning and operation, but the electric system also requires capacity and flexibility services to operate reliably. Electricity generation technologies have different capabilities to provide such services. For example, wind and PV are primarily energy service providers, while the other electricity generation technologies provide capacity and flexibility services in addition to energy. These capacity and flexibility services are difficult to value and depend strongly on the system in which a new generation plant is introduced. These services are represented in electric sector models such as the ReEDS model and corresponding analysis results such as the Standard Scenarios.
The following three figures illustrate the combined impact of CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor projections across the range of resources present in the contiguous United States. The Current Market Conditions LCOE demonstrates the range of LCOE based on macroeconomic conditions similar to the present. The Historical Market Conditions LCOE presents the range of LCOE based on macroeconomic conditions consistent with prior ATB editions and Standard Scenarios model results. The Normalized LCOE (all LCOE estimates are normalized with the lowest Base Year LCOE value) emphasizes the effect of resource quality and the relative differences in the three future pathways independent of project finance assumptions. The ATB representative plant characteristics that best align with recently installed or anticipated near-term utility-scale PV plants are associated with Utility PV: CF 20%. Data for all the resource categories can be found in the ATB data spreadsheet.
The methodology for representing the CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor assumptions behind each pathway is discussed in Projections Methodology. The three pathways are generally defined as:
- High = Base Year (or near-term estimates of projects under construction) equivalent through 2050 maintains current relative technology cost differences
- Mid = technology advances through continued industry growth, public and private R&D investments, and market conditions relative to current levels that may be characterized as "likely" or "not surprising"
- Low = Technology advances that may occur with breakthroughs, increased public and private R&D investments, and/or other market conditions that lead to cost and performance levels that may be characterized as the "limit of surprise" but not necessarily the absolute low bound.
To estimate LCOE, assumptions about the cost of capital to finance electricity generation projects are required. For comparison in the ATB, two project finance structures are represented.
- Current Market Conditions: The values of the production tax credit (PTC) and investment tax credit (ITC) are ramping down by 2020, at which time wind and solar projects may be financed with debt fractions similar to other technologies. This scenario reflects debt interest (4.4% nominal, 1.9% real) and return on equity rates (9.5% nominal, 6.8% real) to represent 2017 market conditions (AEO 2017) and a debt fraction of 60% for all electricity generation technologies. An economic life, or period over which the initial capital investment is recovered, of 20 years is assumed for all technologies. These assumptions are one of the project finance options in the ATB spreadsheet.
- Long-Term Historical Market Conditions: Historically, debt interest and return on equity were represented with higher values. This scenario reflects debt interest (8% nominal, 5.4% real) and return on equity rates (13% nominal, 10.2% real) implemented in the ReEDS model and reflected in prior versions of the ATB and Standard Scenarios model results. A debt fraction of 60% for all electricity generation technologies is assumed. An economic life, or period over which the initial capital investment is recovered, of 20 years is assumed for all technologies. These assumptions are one of the project finance options in the ATB spreadsheet.
These parameters are held constant for estimates representing the Base Year through 2050. No incentives such as the PTC or ITC are included. The equations and variables used to estimate LCOE are defined on the equations and variables page. For illustration of the impact of changing financial structures such as WACC and economic life, see Project Finance Impact on LCOE. For LCOE estimates for High, Mid, and Low scenarios for all technologies, see 2017 ATB Cost and Performance Summary.
In general, the degree of adoption of a range of technology innovations distinguishes the High, Mid and Low cost cases. These projections represent the following trends to reduce CAPEX and FOM.
- Modules
- Increased module efficiencies and increased production-line throughput to decrease CAPEX; overhead costs on a per-kilowatt will go down if efficiency and throughput improvement are realized.
- Reduced wafer thickness or the thickness of thin-film semiconductor layers
- Development of new semiconductor materials
- Development of larger manufacturing facilities in low-cost regions
- Balance of system (BOS)
- Increased module efficiency, reducing the size of the installation
- Development of racking systems that enhance energy production or require less robust engineering
- Integration of racking or mounting components in modules
- Reduction of supply chain complexity and cost
- Creation of standard packages system design
- Improvement supply chains for BOS components in modules
- Improved power electronics
- Improvement of inverter prices and performance, possibly by integrating micro-inverters
- Decreased installation costs and margins
- Reduction of supply chain margins (e.g., profit and overhead charged by suppliers, manufacturer, distributors, and retailers); this will likely occur naturally as the U.S. PV industry grows and matures.
- Streamlining of installation practices through improved workforce development and training, and developing standardized PV hardware
- Expansion of access to a range of innovative financing approaches and business models
- Development of best practices for permitting interconnection, and PV installation such as subdivision regulations, new construction guidelines, and design requirements.
FOM cost reduction represents optimized O&M strategies, reduced component replacement costs, and lower frequency of component replacement.
Concentrating Solar Power
Representative Technology
Concentrating solar power (CSP) technology is assumed to be molten-salt power towers. Thermal energy storage (TES) is accomplished by storing hot molten-salt in a two-tank system, which includes a hot-salt tank and a cold-salt tank. Stored hot salt can be dispatched to the power block as needed, regardless of solar conditions. In the ATB, CSP plants with 10 hours of TES are illustrated.
The first large molten-salt power tower plant (Crescent Dunes 110 MWe with 10 hours of storage) was commissioned in 2015 with a reported installed CAPEX of $8.96/WAC (Danko 2015; Taylor 2016 ).
Resource Potential
Solar resource is prevalent throughout the United States, but the Southwest is particularly suited to CSP plants. The direct normal irradiance (DNI) resource across the Southwest is some of the best in the world and ranges from 2,000 to 2,800 kWh/m2/year. The solar resource for the Southwest was found in Ballaben, Poliafico, and Hashem (2015). The raw resource technical potential of seven western states (Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Texas) exceeds 11,000 GW (almost tenfold current total U.S. electricity generation capacity), assuming an annual average resource > 6.0 kWh/m2/day and after accounting for exclusions such as land slope (>1%), urban areas, water features, and parks, preserves, and wilderness areas (Mehos, Kabel, and Smithers 2009).
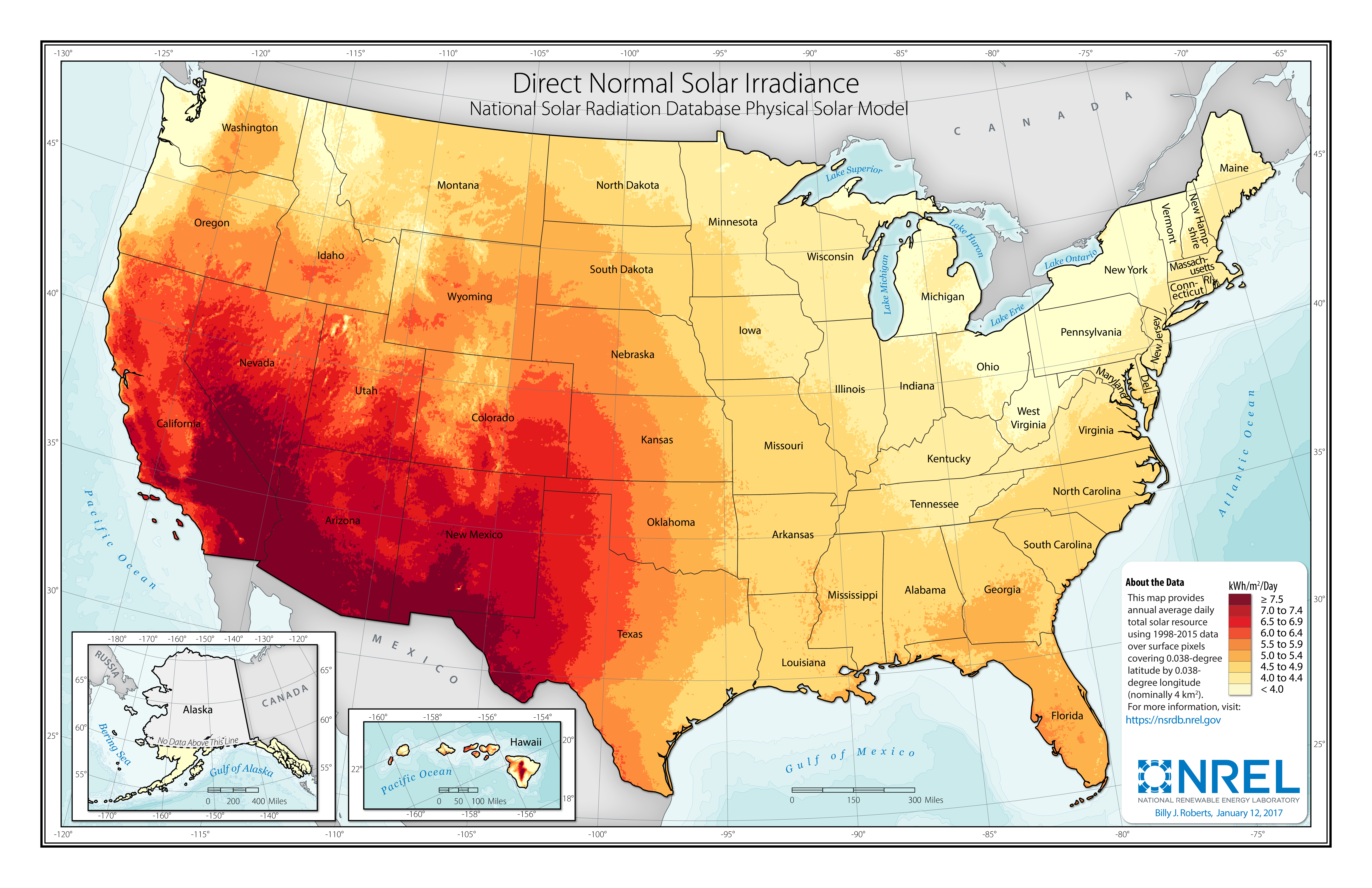
Renewable energy technical potential, as defined by Lopez et al. (2012), represents the achievable energy generation of a particular technology given system performance, topographic limitations, and environmental and land-use constraints. The primary benefit of assessing technical potential is that it establishes an upper-boundary estimate of development potential. It is important to understand that there are multiple types of potential - resource, technical, economic, and market (Lopez et al. 2012; NREL, "Renewable Energy Technical Potential").
The Solar Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement identified 17 solar energy zones for priority development of utility-scale solar facilities in six western states. These zones total 285,000 acres and are estimated to accommodate up to 24 GW of solar potential. The program also allows development, subject to a more rigorous review, on an additional 19 million acres of public land. Development is prohibited on approximately 79 million acres.
According to NREL's Concentrating Solar Power Projects website, 15 of the 17 currently operational CSP plants in the United States use parabolic trough technology. And, two power tower facilities - Ivanpah (392 MW) and Crescent Dunes (110 MW), are operational. One small 5-MW linear Fresnel plant is non-operational in California (NREL's Concentrating Solar Power Projects). This 5-MW solar-enhanced oil recovery site was a development site.
Base Year and Future Year Projections Overview
For the ATB, three representative sites were chosen based on resource class to demonstrate the range of cost and performance across the United States:
- CAPEX are determined using manufacturing cost models and are benchmarked with industry data. The CSP performance and cost are based on the molten-salt power tower technology with dry-cooling to reduce water consumption.
- O&M cost is benchmarked by industry input.
- Capacity factor varies with inclusion of thermal energy storage and solar irradiance. The listed projects assume power towers with 10 hours of thermal energy storage.
- Fair Resource (e.g., Abilene Regional Airport, Texas 5.59 kWh/m2/day based on the site TMY3 file)
- Good Resource (e.g., Las Vegas, Nevada 7.1 kWh/m2/day based on the site TMY3 file)
- Excellent Resource (e.g., Daggett, California 7.46 kWh/m2/day based on the site TMY3 file)
- Representative CSP plant size is net 100 megawatts electrical (MWe).
The Base Year estimates are made for 2015 (via an updated index of the ATB 2016) and for 2018, which has utilized a recent assessment of the industry and has expected project completion in 2018.
Future year projections are informed by published literature and technology pathway assessments to inform CAPEX and O&M cost reductions. Three different projections were developed for scenario modeling as bounding levels:
- High cost: no change in CAPEX, O&M, or capacity factor from 2018 to 2050; consistent across all renewable energy technologies in the ATB
- Mid cost: CAPEX reduced by 25% by 2030 and based on median of literature projections of future CAPEX to 2050; O&M technology pathway analysis.
- Low cost: technology pathway analysis demonstrating feasibility of achieving SunShot targets by 2030 through reductions to CAPEX and O&M.
CAPital EXpenditures (CAPEX): Historical Trends, Current Estimates, and Future Projections
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year. These expenditures include the generation plant, the balance of system (e.g., site preparation, installation, and electrical infrastructure), and financial costs (e.g., development costs, onsite electrical equipment, and interest during construction) and are detailed in CAPEX Definition. In the ATB, CAPEX reflects typical plants and does not include differences in regional costs associated with labor or materials. The range of CAPEX demonstrates variation with resource in the contiguous United States.
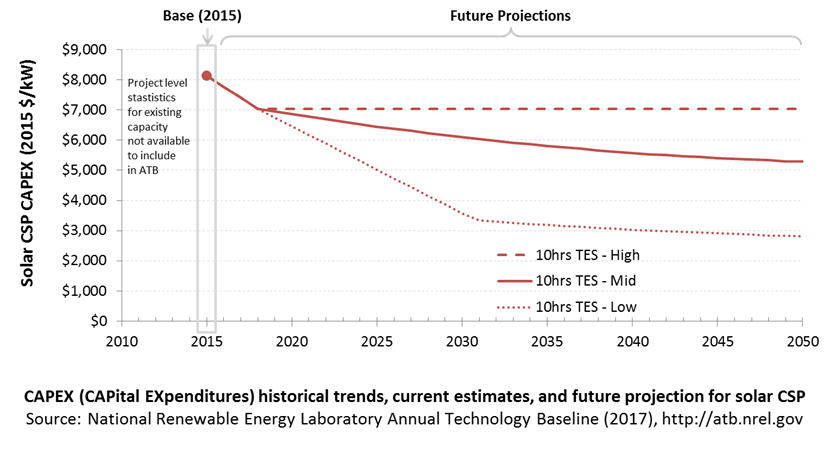
The following figure shows the Base Year estimate and future year projections for CAPEX costs. Three cost reduction scenarios are represented: High, Mid, and Low. The estimate for a given year represents CAPEX of a new plant that reaches commercial operation in that year.
Base Year Estimates
CAPEX is unchanged for resource class because the same plant is assumed to be built in each location. The capacity factor will change with resource.
TES increases plant CAPEX but also increases capacity factor and annual efficiency. TES lowers LCOE for power towers.
The CAPEX estimate (2015) is approximately $8,130/kW. It is for a representative power tower with 10 hours of storage (and a solar multiple of 2.4). Based on recent assessment of the industry and expected project completion in 2018, the CAPEX estimate is $7,037/kW.
Future Year Projections
Three cost projections are developed for CSP technologies:
- High cost: no change in CAPEX, O&M, or capacity factor from 2018 to 2050; consistent across all renewable energy technologies in the ATB
- Mid cost: CAPEX reduced by 25% by 2030 and based on median of literature projections of future CAPEX to 2050; O&M technology pathway analysis
- Low cost: technology pathway analysis demonstrating feasibility of achieving SunShot targets by 2030 through reductions to CAPEX and O&M.
Detailed description of the methodology for developing Future Year Projections is found in Projections Methodology.
Technology innovations that could impact future CAPEX costs are summarized in LCOE Projections.
CAPEX Definition
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year.
The ATB represents the year in which a plant starts commercial operation. Accordingly, for plants whose construction duration exceeds one year, CAPEX costs will represent technology costs that are lagging current-year estimates by at least one year. For CSP plants, the construction period is typically three years.
For the ATB - and based on EIA (2016a), Turchi (2010), and Turchi and Heath (2013) - the CSP generation plant envelope is defined to include:
- CSP generation plant
- Solar collectors
- Solar receiver
- Piping and heat-transfer fluid system
- Power block (heat exchangers, power turbine, generator, cooling system)
- Thermal energy storage system
- Installation
- Balance of system, including installation, land acquisition, electrical infrastructure and project indirect costs
- Land acquisition, site preparation, installation of underground utilities, access roads, fencing, and buildings for operations and maintenance
- Electrical infrastructure, such as transformers, switchgear, and electrical system connecting modules to each other and to control the center; the generator voltage is 13.8 kV, the step-up transformer is 13.8/230kV, and the transmission tie line is 230 kV.
- Project indirect costs, including costs related to engineering, distributable labor and materials, construction management start up and commissioning, and contractor overhead costs, fees, and profit.
- Financial Costs
- Owner's costs, such as development costs, preliminary feasibility and engineering studies, environmental studies and permitting, legal fees, insurance costs, and property taxes during construction
- Onsite electrical equipment (e.g., switchyard), a nominal-distance spur line (<1 mile), and necessary upgrades at a transmission substation; distance-based spur line cost (GCC) not included in the ATB
- Interest during construction estimated based on three-year duration accumulated 80%/10%/10% at half-year intervals and an 8% nominal interest rate (ConFinFactor).
CAPEX can be determined for a plant in a specific geographic location as follows:
CAPEX = ConFinFactor*(OCC*CapRegMult+GCC).
(See the Financial Definitions tab in the ATB data spreadsheet.)
Regional cost variations and geographically specific grid connection costs are not included in the ATB (CapRegMult = 1; GCC = 0). In the ATB, the input value is overnight capital cost (OCC) and details to calculate interest during construction (ConFinFactor).
In the ATB, CAPEX represents a typical solar-CSP plant with 10 hours of thermal storage and does not vary with resource. Regional cost effects associated with labor rates, material costs, and other regional effects as defined by EIA (2016a) expand the range of CAPEX. Unique land-based spur line costs based on distance and transmission line costs expand the range of CAPEX even further. The following figure illustrates the ATB representative plant relative to the range of CAPEX including regional costs across the contiguous United States. The ATB representative plants are associated with a regional multiplier of 1.0.
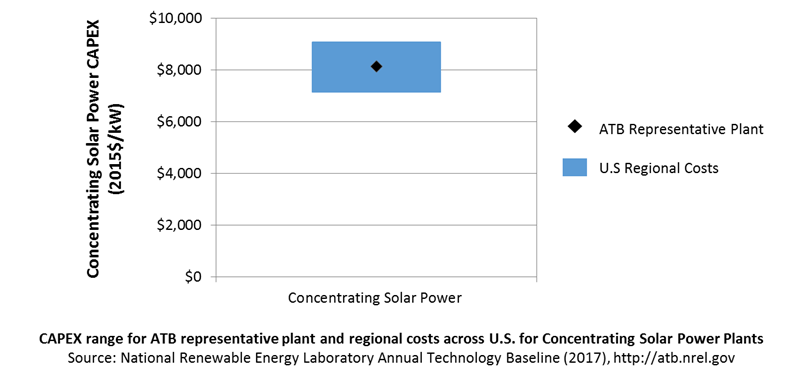
Standard Scenarios Model Results
ATB CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor assumptions for the Base Year and future projections through 2050 for High, Mid, and Low projections are used to develop the NREL Standard Scenarios using the ReEDS model. See ATB and Standard Scenarios.
CAPEX in the ATB does not represent regional variants (CapRegMult) associated with labor rates, material costs, etc., but the ReEDS model does include 134 regional multipliers (EIA 2016a).
The ReEDS model determines the land-based spur line (GCC) uniquely for each potential CSP plant based on distance and transmission line cost.
Operation and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
Operations and maintenance (O&M) costs represent the annual expenditures required to operate and maintain a solar CSP plant over its technical lifetime of 30 years (the distinction between economic life and technical life is described here), including:
- Operating and administrative labor, insurance, legal and administrative fees, and other fixed costs
- Utilities (water, power, natural gas) and mirror washing
- Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance, including replacement parts for solar field and power block components over the technical lifetime of the plant
The following figure shows the Base Year estimate and future year projections for fixed O&M (FOM) costs. Three cost reduction scenarios are represented. The estimate for a given year represents annual average FOM costs expected over the technical lifetime of a new plant that reaches commercial operation in that year.
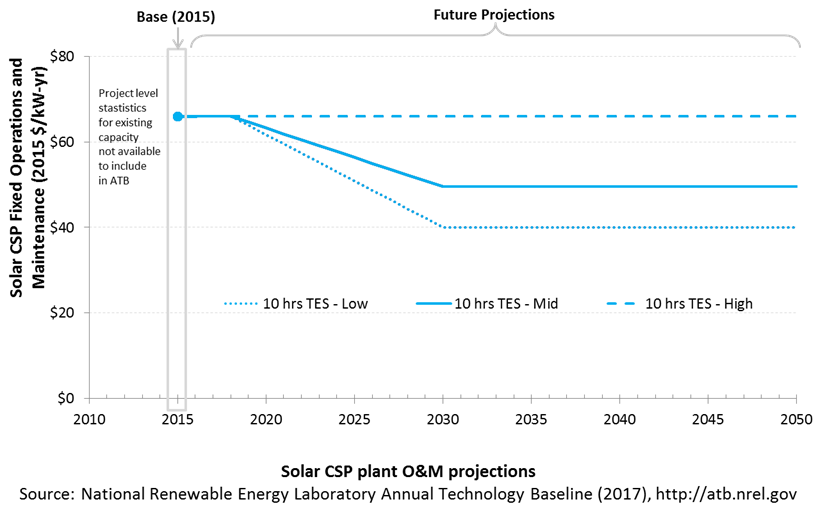
Base Year Estimates
FOM is assumed to be $66/kW-yr. Variable O&M is approximately $4/MWh until 2018 and $3.50/MWh after (Kurup and Turchi 2015).
Future Year Projections
Future FOM is assumed to decline to the SunShot target of $50/kW-yr by 2030 in the Mid cost case and $40/kW-yr by 2030 in the Low cost case (DOE 2012).
A detailed description of the methodology for developing future year projections is found in Projections Methodology.
Technology innovations that could impact future O&M costs are summarized in LCOE Projections.
Capacity Factor: Expected Annual Average Energy Production Over Lifetime
The capacity factor represents the expected annual average energy production divided by the annual energy production, assuming the plant operates at rated capacity for every hour of the year. It is intended to represent a long-term average over the technical lifetime of the plant (the distinction between economic life and technical life is described here). It does not represent interannual variation in energy production. Future year estimates represent the estimated annual average capacity factor over the technical lifetime of a new plant installed in a given year.
Capacity factors are influenced by power block technology, storage technology and capacity, the solar resource, expected downtime, and energy losses. The solar multiple is a design choice that influences the capacity factor.
The following figure shows a range of capacity factors based on variation in the resource for CSP plants in the contiguous United States. The range of the Base Year estimates illustrates the effect of locating a CSP plant at a site with fair, good, or excellent solar resource. The future projections for the High, Mid, and Low cost scenarios are unchanged from the Base Year. Technology improvements are focused on CAPEX and O&M cost elements.
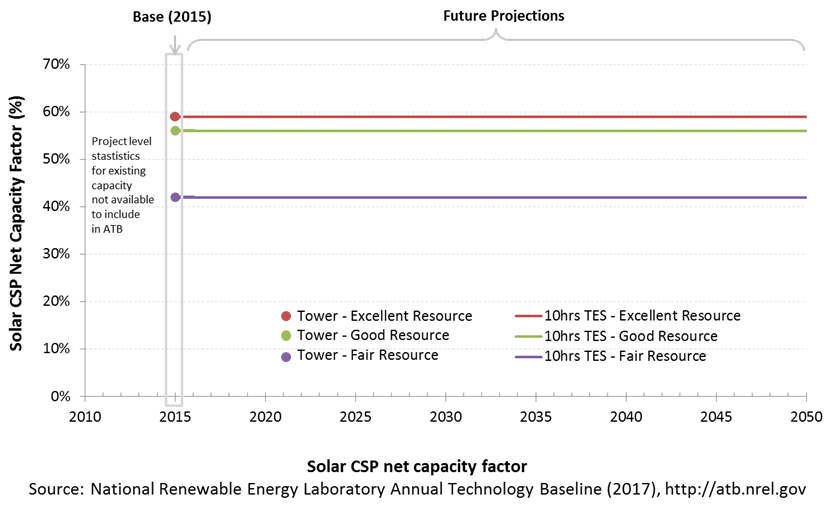
Base Year Estimates
For illustration in the ATB, a range of capacity factors is associated with three resource locations in the contiguous United States, as represented in the ReEDS model for three classes of insolation:
- Fair resource: Abilene, Texas: 5.59 kWh/m2/day based on the site TMY3 file equals 42% capacity factor
- Good resource: Las Vegas, Nevada: 7.1 kWh/m2/day based on the site TMY3 file equals 56% capacity factor
- Excellent resource: Daggett, California: 7.46 kWh/m2/day based on the site TMY3 file equals 59% capacity factor.
Future Year Projections
The CSP technologies are assumed to be power towers, but with different power cycles and operating conditions as time passes:
- 2015: a molten-salt (sodium nitrate/potassium nitrate, aka, solar salt) power tower with direct two-tank TES combined with a steam-Rankine power cycle running at 574°C and 41.2% gross efficiency
- 2018: similar design with identified near-term reductions in heliostat and power system costs
- 2030 Mid: longer-term reductions (e.g., in the heliostats and power system).
- 2030 Low: SunShot targets are met; molten-salt power tower with direct two-tank TES combined with a power cycle running at 700°C and 55% gross efficiency.
Over time, CSP plant output may decline. Capacity factor degradation due to mirror and other component degradation is not accounted for in ATB estimates of capacity factor or LCOE.
The ATB capacity factors are slightly down-rated from SAM 2015 projections.
Estimates of capacity factors for CSP in the ATB represent typical operation. The dispatch characteristics of these systems are valuable to the electric system to manage changes in net electricity demand. Actual capacity factors will be influenced by the degree to which system operators call on CSP plants to manage grid services.
Standard Scenarios Model Results
ATB CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor assumptions for the Base Year and future projections through 2050 for High, Mid, and Low projections are used to develop the NREL Standard Scenarios using the ReEDS model. See ATB and Standard Scenarios.
CSP plants with TES can be dispatched by grid operators to accommodate diurnal and seasonal load variations and output from variable generation sources (wind and solar PV). Because of this, their annual energy production and the value of that generation are determined by the electric system needs and capacity and ancillary services markets.
Plant Cost and Performance Projections Methodology
When comparing the ATB projections with other projections, note that there are major differences in technology assumptions, radiation conditions, field sizes, storage configurations, and other factors.
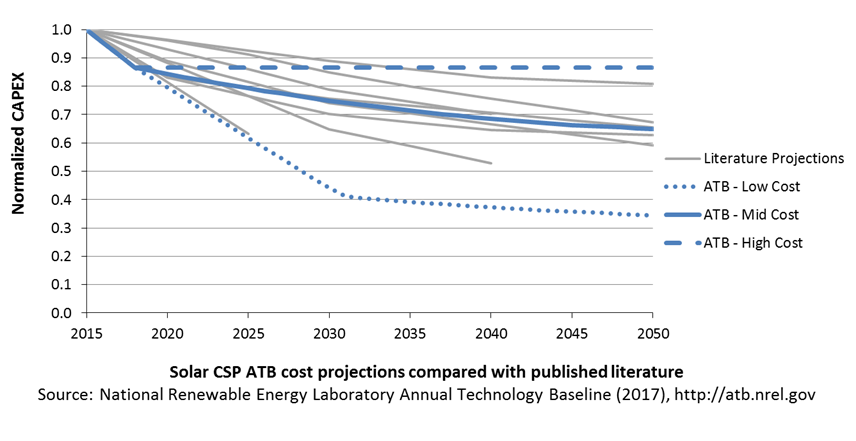
The Low ATB projection is based on the SunShot Vision Study (DOE 2012; Mehos et al. 2016 ) and has been vetted with solar industry representatives.
Attempts have been made to clarify the specifics of the other published CSP projections (e.g., number of hours of storage and solar multiple). As yet, this has not been possible in detail for the ATB 2017.
Projections of future utility-scale CSP plant CAPEX and O&M are based on three different projections developed for scenario modeling as bounding levels:
- High
- Modeled as molten-salt (sodium nitrate/potassium nitrate, aka, solar salt) power tower with direct two-tank TES combined with a steam-Rankine power cycle running at 574°C and 41.2% gross efficiency in 2015
- Costs stay the same from the 2018 estimate through 2050, consistent with ATB renewable energy technologies
- Mid
- Based on published projections that highlight an overall CSP CAPEX reduction by 25% by 2030 and which represent a potential median compared to other published CSP projections until 2050 (Feldman et al. 2016; IRENA 2016)
- Gradual reductions in heliostat and power system cost due to greater deployment volume depicted for 2018 based on current state of industry
- CAPEX and O&M both drop by 25% by 2030
- Low
- Significant reductions in heliostat and power system cost due to greater deployment volume and R&D depicted for 2018; modeled as an advanced molten-salt power tower with direct two-tank TES combined with a power cycle running at 700°C and 55% gross efficiency in 2030 (Mehos et al. 2016)
- Learning rate applied: 9.9% for the solar field and 12% for the turbine based on global projected CSP deployment are applied after 2030
- SunShot CAPEX and O&M targets are met in 2030, including new, high-efficiency power cycles and low-cost heliostats.
Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) Projections
Levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is a simple metric that combines the primary technology cost and performance parameters, CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor. It is included in the ATB for illustrative purposes. The focus of the ATB is to define the primary cost and performance parameters for use in electric sector modeling or other analysis where more sophisticated comparisons among technologies are made. LCOE captures the energy component of electric system planning and operation, but the electric system also requires capacity and flexibility services to operate reliably. Electricity generation technologies have different capabilities to provide such services. For example, wind and PV are primarily energy service providers, while the other electricity generation technologies provide capacity and flexibility services in addition to energy. These capacity and flexibility services are difficult to value and depend strongly on the system in which a new generation plant is introduced. These services are represented in electric sector models such as the ReEDS model and corresponding analysis results such as the Standard Scenarios.
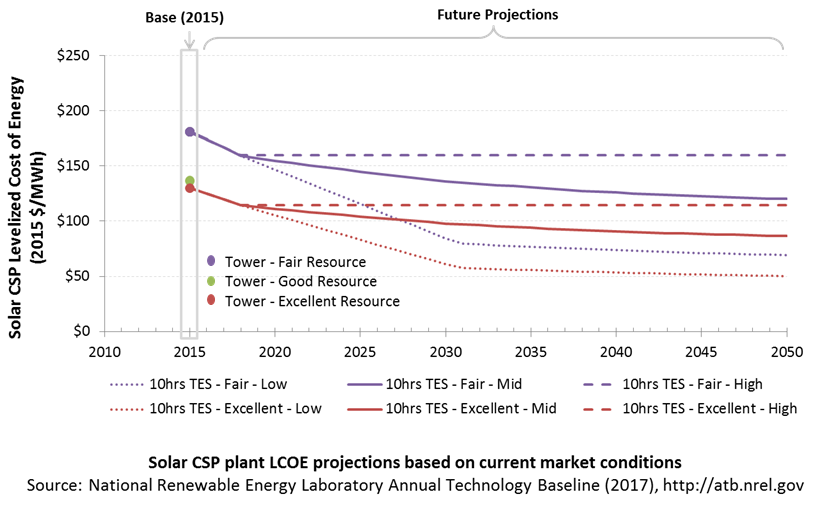
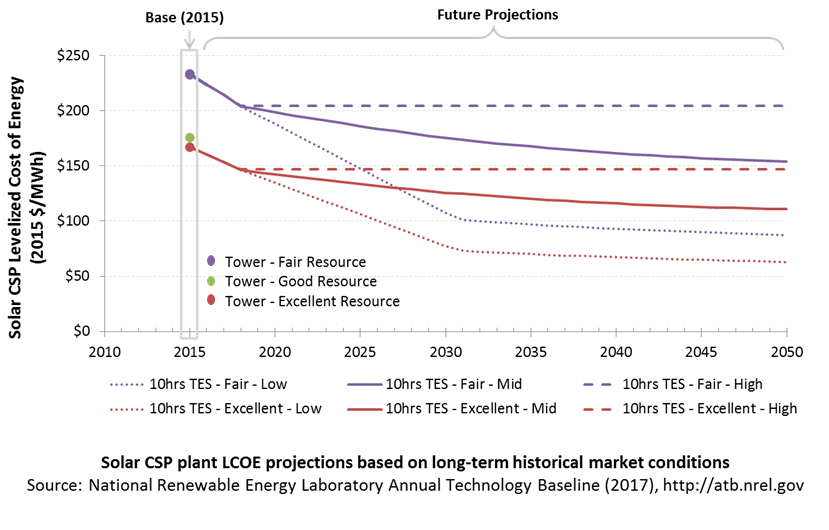
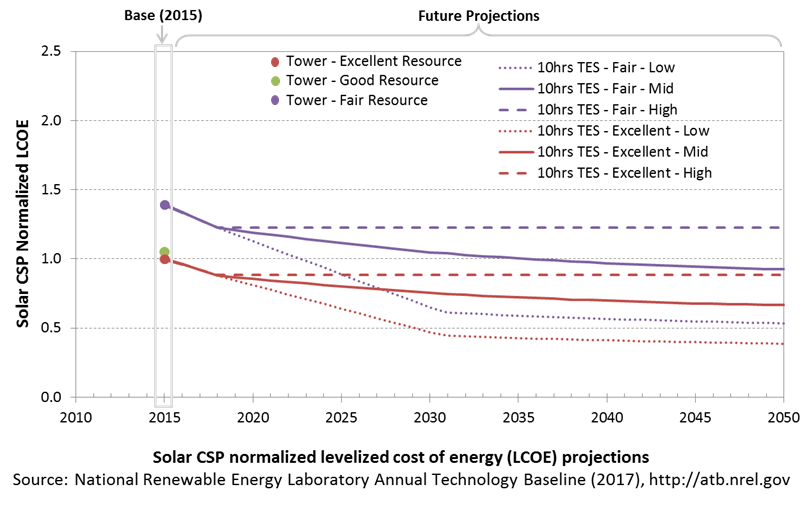
The following three figures illustrate the combined impact of CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor projections across the range of resources present in the contiguous United States. The Current Market Conditions LCOE demonstrates the range of LCOE based on macroeconomic conditions similar to the present. The Historical Market Conditions LCOE presents the range of LCOE based on macroeconomic conditions consistent with prior ATB editions and Standard Scenarios model results. The Normalized LCOE (all LCOE estimates are normalized with the lowest Base Year LCOE value) emphasizes the effect of resource quality and the relative differences in the three future pathways independent of project finance assumptions. The ATB representative plant characteristics that best align with recently installed or anticipated near-term CSP plants are associated with Tower - Excellent Resource. Data for all the resource categories can be found in the ATB data spreadsheet.
The methodology for representing the CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor assumptions behind each pathway is discussed in Projections Methodology. The three pathways are generally defined as:
- High = Base Year (or near-term estimates of projects under construction) equivalent through 2050 maintains current relative technology cost differences
- Mid = technology advances through continued industry growth, public and private R&D investments, and market conditions relative to current levels that may be characterized as "likely" or "not surprising"
- Low = Technology advances that may occur with breakthroughs, increased public and private R&D investments, and/or other market conditions that lead to cost and performance levels that may be characterized as the "limit of surprise" but not necessarily the absolute low bound.
To estimate LCOE, assumptions about the cost of capital to finance electricity generation projects are required. For comparison in the ATB, two project finance structures are represented.
- Current Market Conditions: The values of the production tax credit (PTC) and investment tax credit (ITC) are ramping down by 2020, at which time wind and solar projects may be financed with debt fractions similar to other technologies. This scenario reflects debt interest (4.4% nominal, 1.9% real) and return on equity rates (9.5% nominal, 6.8% real) to represent 2017 market conditions (AEO 2017) and a debt fraction of 60% for all electricity generation technologies. An economic life, or period over which the initial capital investment is recovered, of 20 years is assumed for all technologies. These assumptions are one of the project finance options in the ATB spreadsheet.
- Long-Term Historical Market Conditions: Historically, debt interest and return on equity were represented with higher values. This scenario reflects debt interest (8% nominal, 5.4% real) and return on equity rates (13% nominal, 10.2% real) implemented in the ReEDS model and reflected in prior versions of the ATB and Standard Scenarios model results. A debt fraction of 60% for all electricity generation technologies is assumed. An economic life, or period over which the initial capital investment is recovered, of 20 years is assumed for all technologies. These assumptions are one of the project finance options in the ATB spreadsheet.
These parameters are held constant for estimates representing the Base Year through 2050. No incentives such as the PTC or ITC are included. The equations and variables used to estimate LCOE are defined on the equations and variables page. For illustration of the impact of changing financial structures such as WACC and economic life, see Project Finance Impact on LCOE. For LCOE estimates for High, Mid, and Low scenarios for all technologies, see 2017 ATB Cost and Performance Summary.
In general, the degree of adoption of a range of technology innovations distinguishes the High, Mid and Low cost cases. These projections represent the following trends to reduce CAPEX and FOM, and increase O&M.
- Power tower improvements
- Better and longer-lasting selective surface coatings improve receiver efficiency and reduce O&M costs
- New salts allow for higher operating temperatures and lower-cost TES
- Development of the power cycle running at 700°C and 55% gross efficiency improves cycle efficiency, reduces powerblock cost, and reduces O&M costs
- Lower-cost heliostats developed due to more efficient designs and automated and high-volume manufacturing
- General and "soft" costs improvements
- Expansion of world market leads to greater and more efficient supply chains; reduction of supply chain margins (e.g., profit and overhead charged by suppliers, manufacturer, distributors, and retailers)
- Expansion of access to a range of innovative financing approaches and business models
- Development of best practices for permitting interconnection and installation such as subdivision regulations, new construction guidelines, and design requirements.
The LCOE range shown is based on locations with fair (Abilene, Texas), good (Las Vegas, Nevada), and excellent (Daggett, California) resources. The CAPEX is the same at each resource as the same plant is used.
Biopower Plants
In a biopower plant:
- Heat is created: Biomass (sometimes co-fired with coal) is pulverized, mixed with hot air, and burned in suspension.
- Water turns to steam: The heat turns purified water into steam, which is piped to the turbine.
- Steam turns the turbine: The pressure of the steam pushes the turbine blade, turns the shaft in the generator, and creates power.
- Steam is turned back into water: Cool water is drawn into a condenser where the steam turns back into water that can be reused in the plant.

(a biomass gasifier that operates on wood chips)

Renewable energy technical potential, as defined by Lopez et al. (2012), represents the achievable energy generation of a particular technology given system performance, topographic limitations, and environmental and land-use constraints. Technical resource potential for biopower is based on estimated biomass quantities from the Billion Ton Update study (DOE 2011).
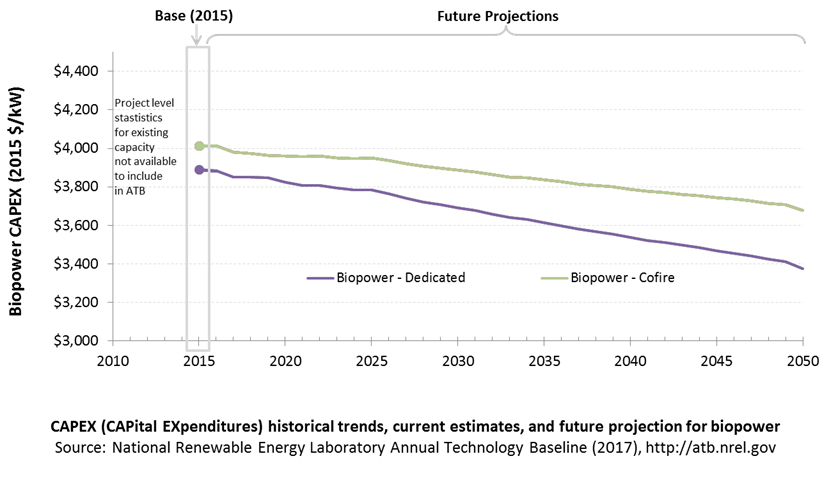
CAPital EXpenditures (CAPEX): Historical Trends, Current Estimates, and Future Projections
Because biopower plants are well-known and perform close to their optimal performance, EIA expects capital expenditures (CAPEX) will incrementally improve over time and slightly more quickly than inflation.
The exception is new biomass cofiring, which is expected to have costs that decline a bit more than existing cofiring project technologies.
CAPEX Definition
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year.
Overnight capital costs are modified from EIA (2014). Capital costs include overnight capital cost plus defined transmission cost, and it removes a material price index. The overnight capital costs for cofired units are not the cost of upgrading a plant but the total cost of the plant after the upgrade.
Fuel costs are taken from the Billion Ton Update study (DOE 2011).
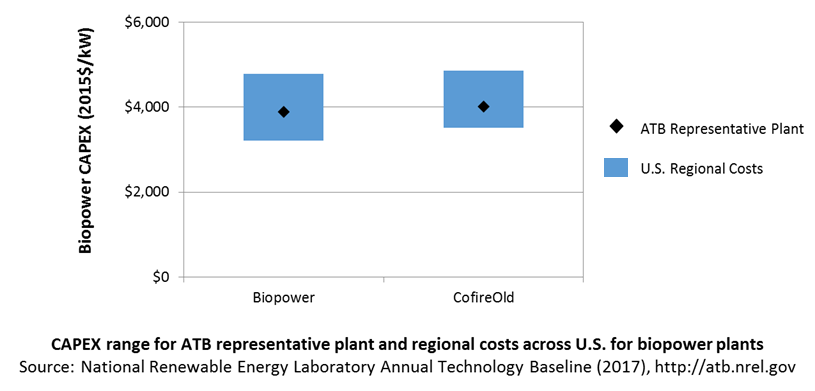
| Overnight Capital Cost ($/kW) | Construction Financing Factor (ConFinFactor) | CAPEX ($/kW) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dedicated: Dedicated biopower plant | $3,737 | 1.041 | $3,889 |
| CofireOld: Pulverized coal with sulfur dioxide (SO2) scrubbers and biomass co-firing | $3,856 | 1.041 | $4,013 |
| CofireNew: Advanced supercritical coal with SO2 and NOx controls and biomass co-firing | $3,856 | 1.041 | $4,013 |
CAPEX can be determined for a plant in a specific geographic location as follows:
CAPEX = ConFinFactor*(OCC*CapRegMult+GCC).
(See the Financial Definitions tab in the ATB data spreadsheet.)
Regional cost variations and geographically specific grid connection costs are not included in the ATB (CapRegMult = 1; GCC = 0). In the ATB, the input value is overnight capital cost (OCC) and details to calculate interest during construction (ConFinFactor).
In the ATB, CAPEX represents each type of biopower plant with a unique value. Regional cost effects associated with labor rates, material costs, and other regional effects as defined by EIA (2016a) expand the range of CAPEX. Unique land-based spur line costs based on distance and transmission line costs are not estimated. The following figure illustrates the ATB representative plant relative to the range of CAPEX including regional costs across the contiguous United States. The ATB representative plants are associated with a regional multiplier of 1.0.
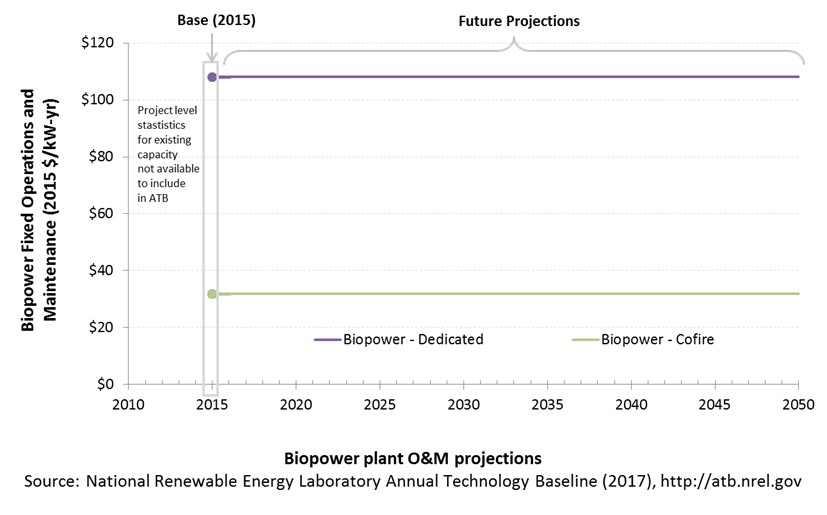
Operation and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
Operations and maintenance (O&M) costs represent the annual expenditures required to operate and maintain a plant over its technical lifetime (the distinction between economic life and technical life is described here), including:
- Insurance, taxes, land lease payments, and other fixed costs
- Present value and annualized large component replacement costs over technical life
- Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance of power plants, transformers, and other components over the technical lifetime of the plant.
Market data for comparison are limited and generally inconsistent in the range of costs covered and the length of the historical record.
Capacity Factor: Expected Annual Average Energy Production Over Lifetime
The capacity factor represents the assumed annual energy production divided by the total possible annual energy production, assuming the plant operates at rated capacity for every hour of the year. For biopower plants, the capacity factors are typically lower than their availability factors. Biopower plant availability factors have a wide range depending on system design, fuel type and availability, and maintenance schedules.
Biopower plants are typically baseload plants with steady capacity factors. For the ATB, the biopower capacity factor is taken as the average capacity factor for biomass plants for 2015, as reported by EIA.
Biopower capacity factors are influenced by technology and feedstock supply, expected downtime, and energy losses.

Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) Projections
Levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is a simple metric that combines the primary technology cost and performance parameters, CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor. It is included in the ATB for illustrative purposes. The focus of the ATB is to define the primary cost and performance parameters for use in electric sector modeling or other analysis where more sophisticated comparisons among technologies are made. LCOE captures the energy component of electric system planning and operation, but the electric system also requires capacity and flexibility services to operate reliably. Electricity generation technologies have different capabilities to provide such services. For example, wind and PV are primarily energy service providers, while the other electricity generation technologies provide capacity and flexibility services in addition to energy. These capacity and flexibility services are difficult to value and depend strongly on the system in which a new generation plant is introduced. These services are represented in electric sector models such as the ReEDS model and corresponding analysis results such as the Standard Scenarios.
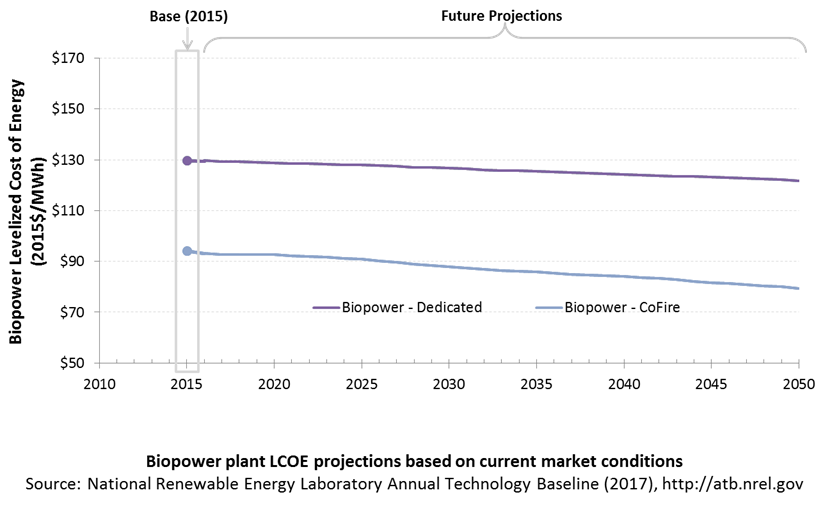
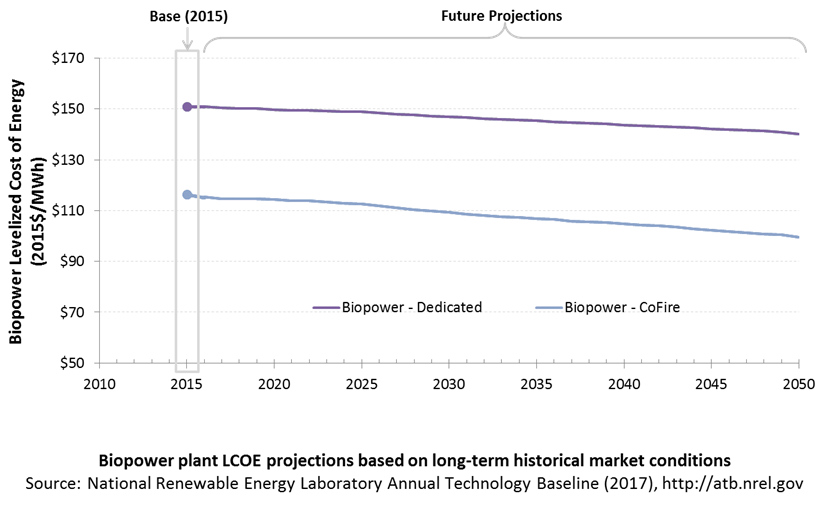
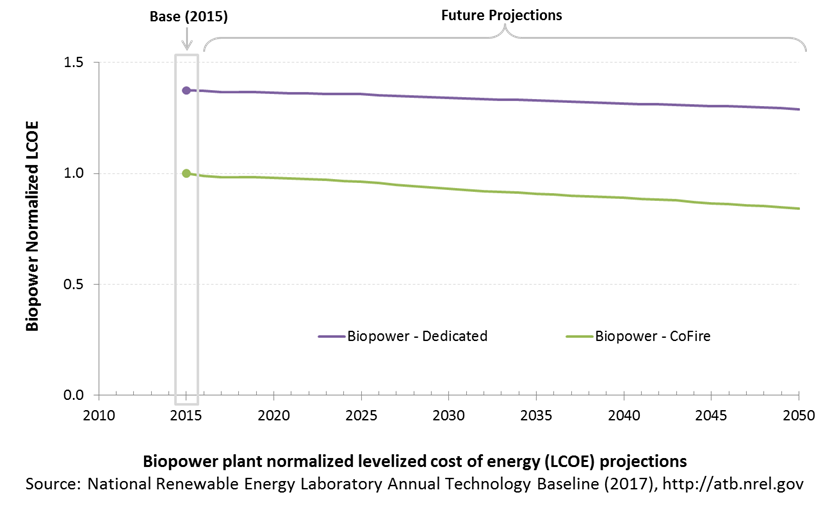
The following three figures illustrate the combined impact of CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor projections across the range of resources present in the contiguous United States. The Current Market Conditions LCOE demonstrates the range of LCOE based on macroeconomic conditions similar to the present. The Historical Market Conditions LCOE presents the range of LCOE based on macroeconomic conditions consistent with prior ATB editions and Standard Scenarios model results. The Normalized LCOE (all LCOE estimates are normalized with the lowest Base Year LCOE value) emphasizes the relative effect of fuel price and heat rate independent of project finance assumptions. Data for all the resource categories can be found in the ATB data spreadsheet.
The LCOE of biopower plants is directly impacted by the differences in CAPEX (installed capacity costs) as well as by heat rate differences. For a given year, the LCOE assumes that the fuel prices from that year continue throughout the lifetime of the plant.
Regional variations will ultimately impact biomass feedstock costs, but these are not included in the ATB.
The projections do not include any cost of carbon.
Fuel prices are based on the EIA's Annual Energy Outlook 2017 (EIA 2017).
To estimate LCOE, assumptions about the cost of capital to finance electricity generation projects are required. For comparison in the ATB, two project finance structures are represented.
- Current Market Conditions: The values of the production tax credit (PTC) and investment tax credit (ITC) are ramping down by 2020, at which time wind and solar projects may be financed with debt fractions similar to other technologies. This scenario reflects debt interest (4.4% nominal, 1.9% real) and return on equity rates (9.5% nominal, 6.8% real) to represent 2017 market conditions (AEO 2017) and a debt fraction of 60% for all electricity generation technologies. An economic life, or period over which the initial capital investment is recovered, of 20 years is assumed for all technologies. These assumptions are one of the project finance options in the ATB spreadsheet.
- Long-Term Historical Market Conditions: Historically, debt interest and return on equity were represented with higher values. This scenario reflects debt interest (8% nominal, 5.4% real) and return on equity rates (13% nominal, 10.2% real) implemented in the ReEDS model and reflected in prior versions of the ATB and Standard Scenarios model results. A debt fraction of 60% for all electricity generation technologies is assumed. An economic life, or period over which the initial capital investment is recovered, of 20 years is assumed for all technologies. These assumptions are one of the project finance options in the ATB spreadsheet.
These parameters are held constant for estimates representing the Base Year through 2050. No incentives such as the PTC or ITC are included. The equations and variables used to estimate LCOE are defined on the equations and variables page. For illustration of the impact of changing financial structures such as WACC and economic life, see Project Finance Impact on LCOE. For LCOE estimates for High, Mid, and Low scenarios for all technologies, see 2017 ATB Cost and Performance Summary.
References
Bolinger, Mark, and Joachim Seel. 2016. Utility-Scale Solar 2015: An Empirical Analysis of Project Cost, Performance, and Pricing Trends in the United States. Berkeley, CA: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. LBNL-1006037. August 2016. https://emp.lbl.gov/sites/all/files/lbnl-1006037_report.pdf.
Danko, Pete. 2015. 'SolarReserve: Crescent Dunes Solar Tower Will Power Up in March: Without Ivanpah's Woes.' Breaking Energy. February 10, 2015. http://breakingenergy.com/2015/02/10/solarreserve-crescent-dunes-solar-tower-will-power-up-in-march-without-ivanpahs-woes/.
Denholm, P., and R. Margolis. 2008. 'Land-Use Requirements and the Per-Capita Solar Footprint for Photovoltaic Generation in the United States.' Energy Policy (36):3531–3543.
DOE (U.S. Department of Energy). 2011. U.S. Billion-Ton Update: Biomass Supply for a Bioenergy and Bioproducts Industry. Perlack, R.D., and B.J. Stokes, eds. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. ORNL/TM-2011/224. August 2011. https://www.osti.gov/scitech/biblio/1023318.
DOE (U.S. Department of Energy). 2012. SunShot Vision Study. DOE/GO-102012-3037. February 2012. https://www1.eere.energy.gov/solar/pdfs/47927.pdf.
EIA (U.S. Energy Information Administration). 2014. Annual Energy Outlook 2014 with Projections to 2040. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Energy. DOE/EIA-0383(2014). April 2014. http://www.eia.gov/forecasts/aeo/pdf/0383(2014).pdf.
EIA (U.S. Energy Information Administration). 2016a. Capital Cost Estimates for Utility Scale Electricity Generating Plants. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Energy. November 2016. https://www.eia.gov/analysis/studies/powerplants/capitalcost/pdf/capcost_assumption.pdf.
EIA (U.S. Energy Information Administration). 2017. Annual Energy Outlook 2017 with Projections to 2050. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Energy. January 5, 2017. http://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/pdf/0383(2017).pdf.
Eurek, Kelly, Patrick Sullivan, Michael Gleason, Dylan Hettinger, Donna Heimiller, and Anthony Lopez. 2017. "An Improved Global Wind Resource Estimate for Integrated Assessment Models." Energy Economics 64(May 2017): 552–567
Feldman, David, Robert Margolis, Paul Denholm, and Joseph Stekli. 2016. Exploring the Potential Competitiveness of Utility-Scale Photovoltaics plus Batteries with Concentrating Solar Power, 2015–2030. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-6A20-66592. August 2016. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy16osti/66592.pdf.
Fu, Ran, Donald Chung, Travis Lowder, David Feldman, Kristen Ardani, and Robert Margolis. 2016. U.S. Photovoltaic (PV) Prices and Cost Breakdowns: Q1 2016 Benchmarks for Residential, Commercial, and Utility-Scale Systems. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/PR-6A20-67142. September 2016. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy16osti/67142.pdf.
IRENA (International Renewable Energy Agency). 2016. The Power to Change: Solar and Wind Cost Reduction Potential to 2025. June 2016. Paris: International Renewable Energy Agency. http://www.irena.org/DocumentDownloads/Publications/IRENA_Power_to_Change_2016.pdf.
Jordan, Dirk C., and Sarah R. Kurtz. 2013. Photovoltaic Degradation Rates: An Analytical Review. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/JA-5200-51664. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/pip.1182/full.
Kurup, Parthiv, and Craig S. Turchi. 2015. Parabolic Trough Collector Cost Update for the System Advisor Model (SAM). Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-6A20-65228. November 2015. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy16osti/65228.pdf.
Lopez, Anthony, Billy Roberts, Donna Heimiller, Nate Blair, and Gian Porro. 2012. U.S. Renewable Energy Technical Potentials: A GIS-Based Analysis. National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-6A20-51946. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy12osti/51946.pdf.
Mehos, Mark, Craig Turchi, Jennie Jorgenson, Paul Denholm, Clifford Ho, and Kenneth Armijo. 2016. On the Path to SunShot: Advancing Concentrating Solar Power Technology, Performance, and Dispatchability. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-5500-65688. May 2016. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy16osti/65688.pdf.
Taylor, Phil. 2016. 'Nev. Plant Solves Quandary of How to Store Sunshine.' E&E News. March 29, 2016. http://www.eenews.net/stories/1060034748.
Turchi, C. 2010. Parabolic Trough Reference Plant for Cost Modeling with the Solar Advisor Model (SAM). Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-550-47605. July 2010. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy10osti/47605.pdf.
Turchi, Craig S., and Garvin A. Heath. 2013. Molten Salt Power Tower Cost Model for the System Advisor Model (SAM). Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-5500-57625. February 2013. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy13osti/57625.pdf.
Wiser, Ryan, Karen Jenni, Joachim Seel, Erin Baker, Maureen Hand, Eric Lantz, and Aaron Smith. 2016. Forecasting Wind Energy Costs and Cost Drivers: The Views of the World's Leading Experts. Berkeley, CA: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. LBNL-1005717. June 2016. https://emp.lbl.gov/publications/forecasting-wind-energy-costs-and.
Woodhouse, Michael, Rebecca Jones-Albertus, David Feldman, Ran Fu, Kelsey Horowitz, Donald Chung, Dirk Jordan, and Sarah Kurtz. 2016. On the Path to SunShot: The Role of Advancements in Solar Photovoltaic Efficiency, Reliability, and Costs. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-6A20-65464. May 2016. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy16osti/65872.pdf.