Annual Technology Baseline 2018
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
Recommended Citation:
NREL (National Renewable Energy Laboratory). 2018. 2018 Annual Technology Baseline. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. http://atb.nrel.gov/.
Please consult Guidelines for Using ATB Data:
https://atb.nrel.gov/electricity/user-guidance.html
Concentrating Solar Power
CAPEX Definition
Capital expenditures (CAPEX) are expenditures required to achieve commercial operation in a given year.
The ATB represents the year in which a plant starts commercial operation. Accordingly, for plants whose construction duration exceeds one year, CAPEX costs will represent technology costs that are lagging current-year estimates by at least one year. For CSP plants, the construction period is typically three years.
For the ATB-and based on based on EIA 2016a, Turchi et al 2010, and Turchi and Heath 2013 - the CSP generation plant envelope is defined to include:
- CSP generation plant
- Solar collectors
- Solar receiver
- Piping and heat-transfer fluid system
- Power block (heat exchangers, power turbine, generator, and cooling system)
- Thermal energy storage system
- Installation
- Balance of system, including installation, land acquisition, electrical infrastructure, and project indirect costs
- Land acquisition, site preparation, and installation of underground utilities, access roads, fencing, and buildings for operations and maintenance
- Electrical infrastructure, such as transformers, switchgear, and electrical system connecting modules to each other and to control the center; the generator voltage is 13.8 kV, the step-up transformer is 13.8/230kV, and the transmission tie line is 230 kV
- Project indirect costs, including costs related to engineering, distributable labor and materials, construction management start up and commissioning, and contractor overhead costs, fees, and profit
- Financial costs
- Owners' costs, such as development costs, preliminary feasibility and engineering studies, environmental studies and permitting, legal fees, insurance costs, and property taxes during construction
- Onsite electrical equipment (e.g., switchyard), a nominal-distance spur line (< 1 mile), and necessary upgrades at a transmission substation; distance-based spur line cost (GCC) not included in the ATB
- Interest during construction estimated based on three-year duration accumulated 80%/10%/10% at half-year intervals and a nominal interest rate (ConFinFactor).
CAPEX can be determined for a plant in a specific geographic location as follows:
Regional cost variations and geographically specific grid connection costs are not included in the ATB (CapRegMult = 1; GCC = 0). In the ATB, the input value is overnight capital cost (OCC) and details to calculate interest during construction (ConFinFactor).
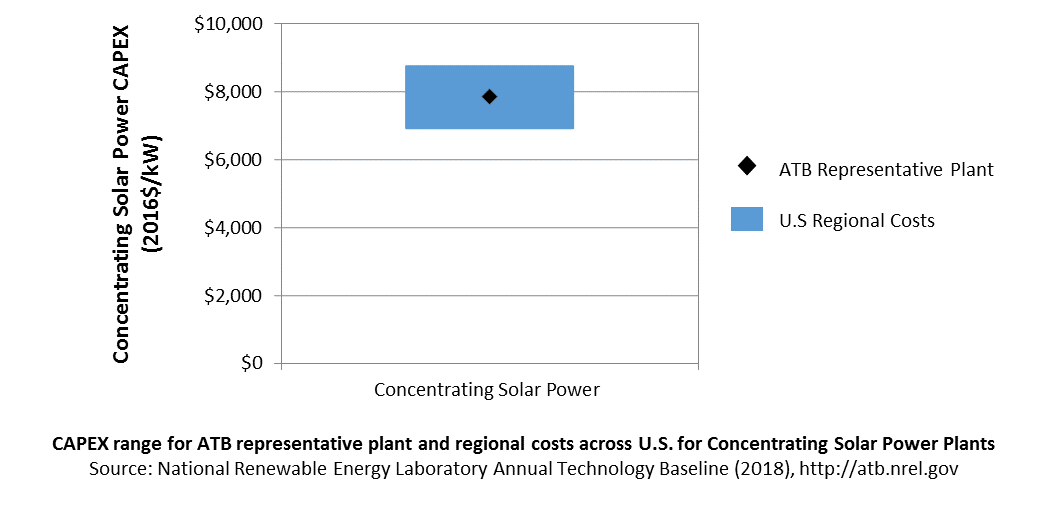
In the ATB, CAPEX represents a typical solar-CSP plant with 10 hours of thermal storage and does not vary with resource. Regional cost effects associated with labor rates, material costs, and other regional effects as defined by EIA 2016a expand the range of CAPEX. Unique land-based spur line costs based on distance and transmission line costs expand the range of CAPEX even further. The following figure illustrates the ATB representative plant relative to the range of CAPEX including regional costs across the contiguous United States. The ATB representative plants are associated with a regional multiplier of 1.0.
Standard Scenarios Model Results
ATB CAPEX, O&M, and capacity factor assumptions for the Base Year and future projections through 2050 for Constant, Mid, and Low technology cost scenarios are used to develop the NREL Standard Scenarios using the ReEDS model. See ATB and Standard Scenarios.
CAPEX in the ATB does not represent regional variants (CapRegMult) associated with labor rates, material costs, etc., but the ReEDS model does include 134 regional multipliers (EIA 2016a).
The ReEDS model determines the land-based spur line (GCC) uniquely for each potential CSP plant based on distance and transmission line cost.
References
EIA (U.S. Energy Information Administration). 2016a. Capital Cost Estimates for Utility Scale Electricity Generating Plants. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Energy. November 2016. https://www.eia.gov/analysis/studies/powerplants/capitalcost/pdf/capcost_assumption.pdf.
Turchi, Craig S., and Garvin A. Heath. 2013. Molten Salt Power Tower Cost Model for the System Advisor Model (SAM). Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-5500-57625. February 2013. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy13osti/57625.pdf.
Turchi, Craig, Mark Mehos, Clifford K. Ho, and Gregory J. Kolb. 2010. Current and Future Costs for Parabolic Trough and Power Tower Systems in the US Market. Preprint. Presented at SolarPACES 2010, Perpignan, France, September 21-24, 2010. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/CP-5500-49303. October 2010. http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy11osti/49303.pdf.
